Sony KV (BN-1)
This article covers how to RGB mod your Sony KV-9PT50, KV-9PT60 or any BN-1 chassis based Sony CRT.
Sony KV-9PT50 (BN-1) chassis CRT RGB mod
I want to share with you a delightful 9" Sony CRT - KV-9PT50 that I've worked on. Although the CRT and tube had experienced some usage, they were reasonably average in quality. Over time, the white plastic housing had become slightly brittle due to internal heat and some parts of it had some cracks. After meticulously sealing the cracks with epoxy and super glue and implementing the RGB modification, the overall appearance significantly improved. My goal was to achieve a professional finish without any switches, massive SCART port, or multiple BNC ports. Fortunately, the XRGB specs came to the rescue, enabling me to achieve this desired outcome. Hardest part of the mod was to create the custom cable - I think I have a potential solution for this in future.

This tutorial should also cover the RGB mod for the below models with the BN-1 chassis. However, there might be differences in chassis, internals etc. KV-9PT60 has a different chassis.
9" models
- KV-9PT50 (white)
- KV-9PT60 (black)
CRT safety
Caution
You can die doing this! So read carefully! CRT TV is not a toy. Do not open a CRT TV. If you don't have any prior knowledge about handling high voltage devices, this guide is not for you. CRT TV contains high enough voltage (20,000+ V) and current to be deadly, even when it is turned off.
Plan of attack
Theory
Sometimes it is nice to know the theory behind the mod. I have put this on a separate page. This shows how the various resistor values are calculated.
Service manuals
Specs
Sony KV-9PT50
- Manufactured: August 1997, Mexico
- NTSC, 60 Hz - 53W
- Chassis: BN-1, SCC-J59A-A
- Tube: A23LDU10X, Sony, Made in Japan
- Jungle Chip: Sony CXA1464 AS (IC301)
Schematics
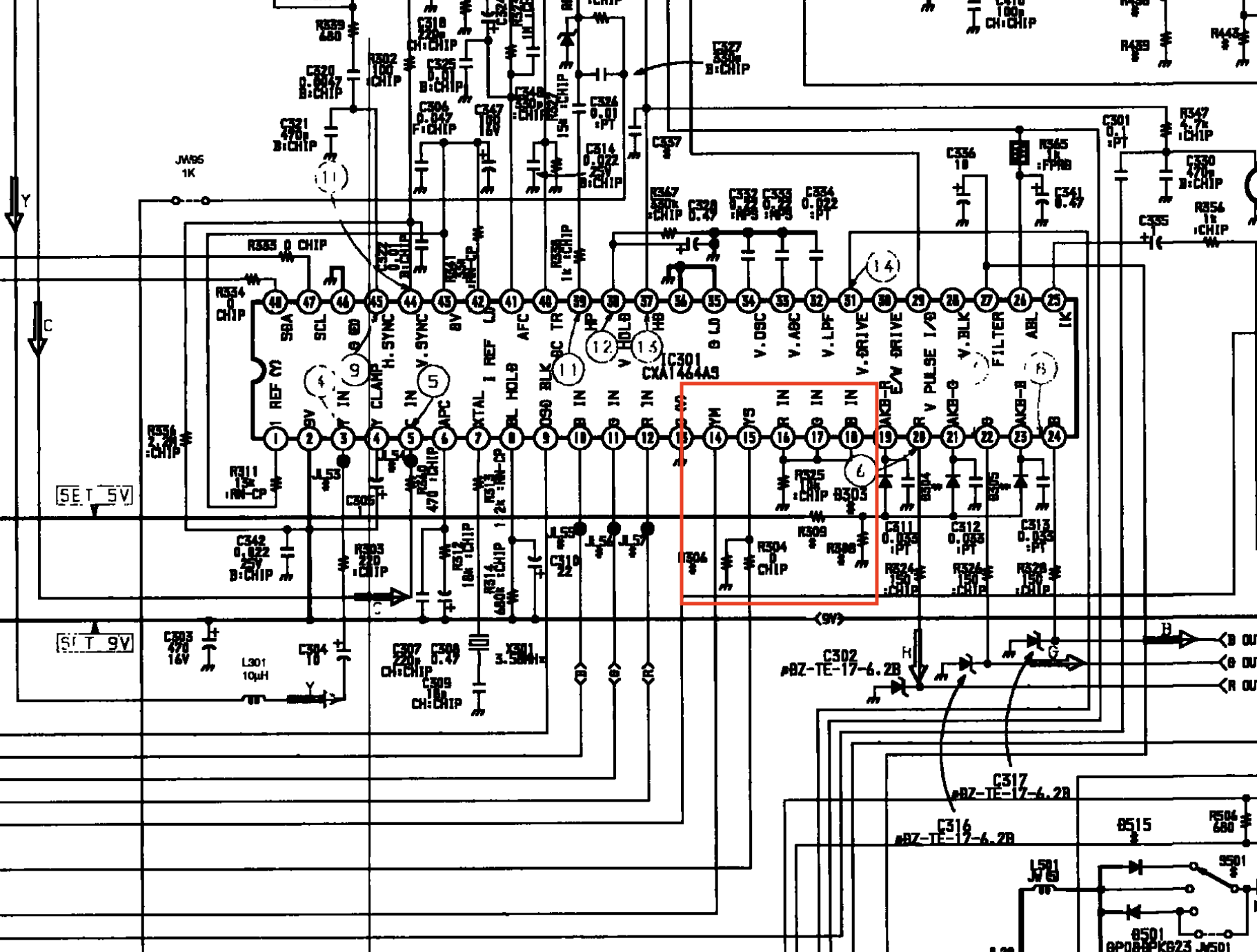
Blanking (Ys), Red, Green, Blue lines are exposed on pin 15, 16, 17, 18 of the CXA1464A9 chroma IC.
Performing the mod
You can't ask for a more straightforward RGB mod.
Fortunately this chassis doesn't require any muxing. You can pass R, G, B through a 0.1uF, 75ohm terminated wire directly to the chroma IC301. Blanking (Ys) can be fed through a 1kΩ + 0.7V didoe to pin 15 of the chroma.
STEP 1: Free the RGB inputs
- Remove the R325 ground resistor (10kΩ) from the board.
- Carefully cut the traces on the board to ensure that the R, G, and B traces are no longer connected or shorted together.
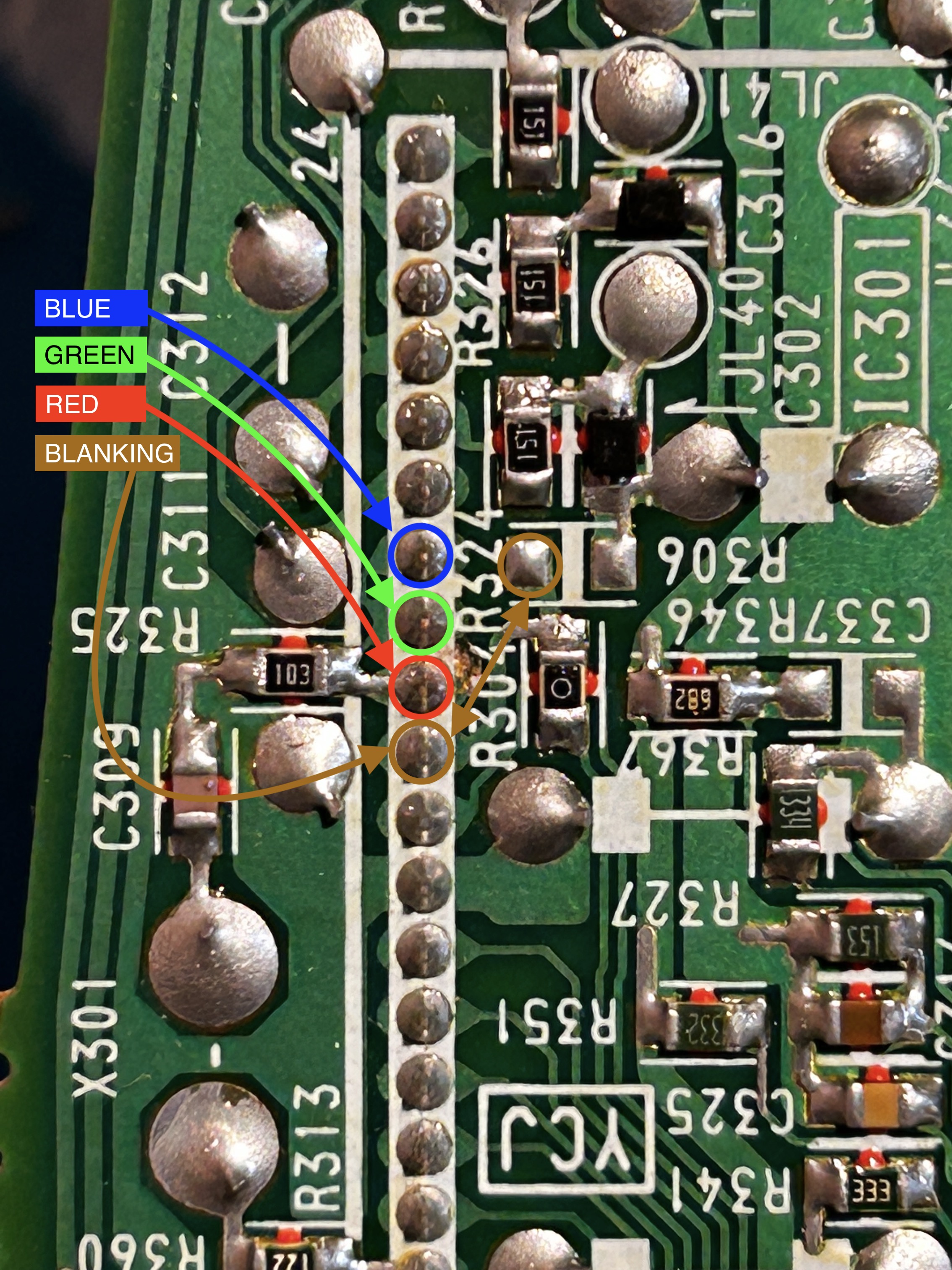
This method provides the best approach that can be easily reversed back. It is important to avoid cutting the pins on the chroma IC as you can easily damage those pins. Replacement chroma IC can be difficult to find, so it's strongly advised against cutting the pins.
On the other hand, cutting the traces is a relatively straightforward process. To do so, you can use a small sharp hobby knife or a screwdriver to carefully scratch away the traces.
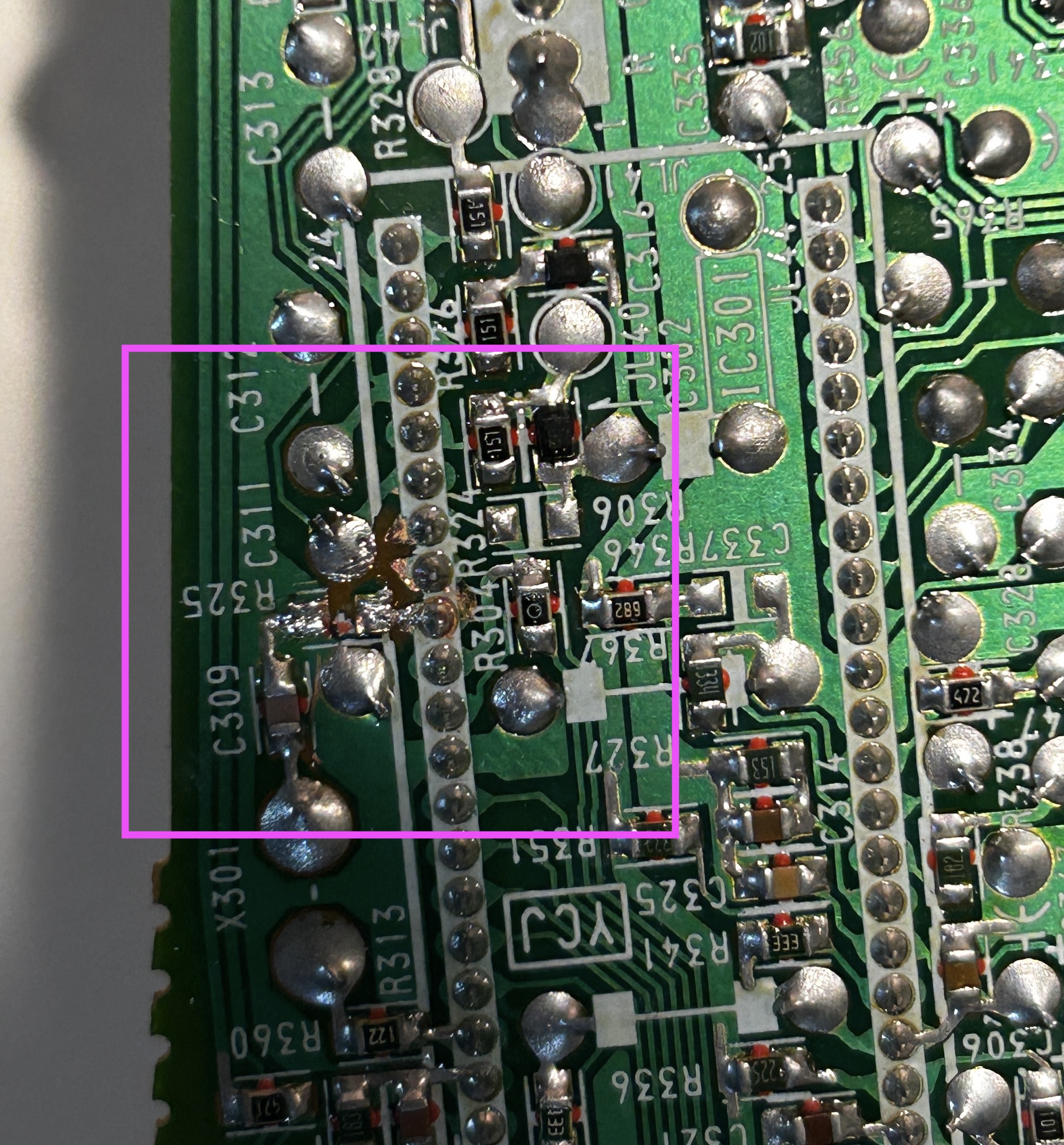
STEP 2: Connect RGB and Blanking
You don't need a long ribbon cable for this mod. Shorter the cable the better as it reduces interferece.
See picture below to see where R, G, B and blanking wires should be connected. Blanking (Ys), Red, Green, Blue lines are exposed on chroma pin 15, 16, 17, 18 respectively.
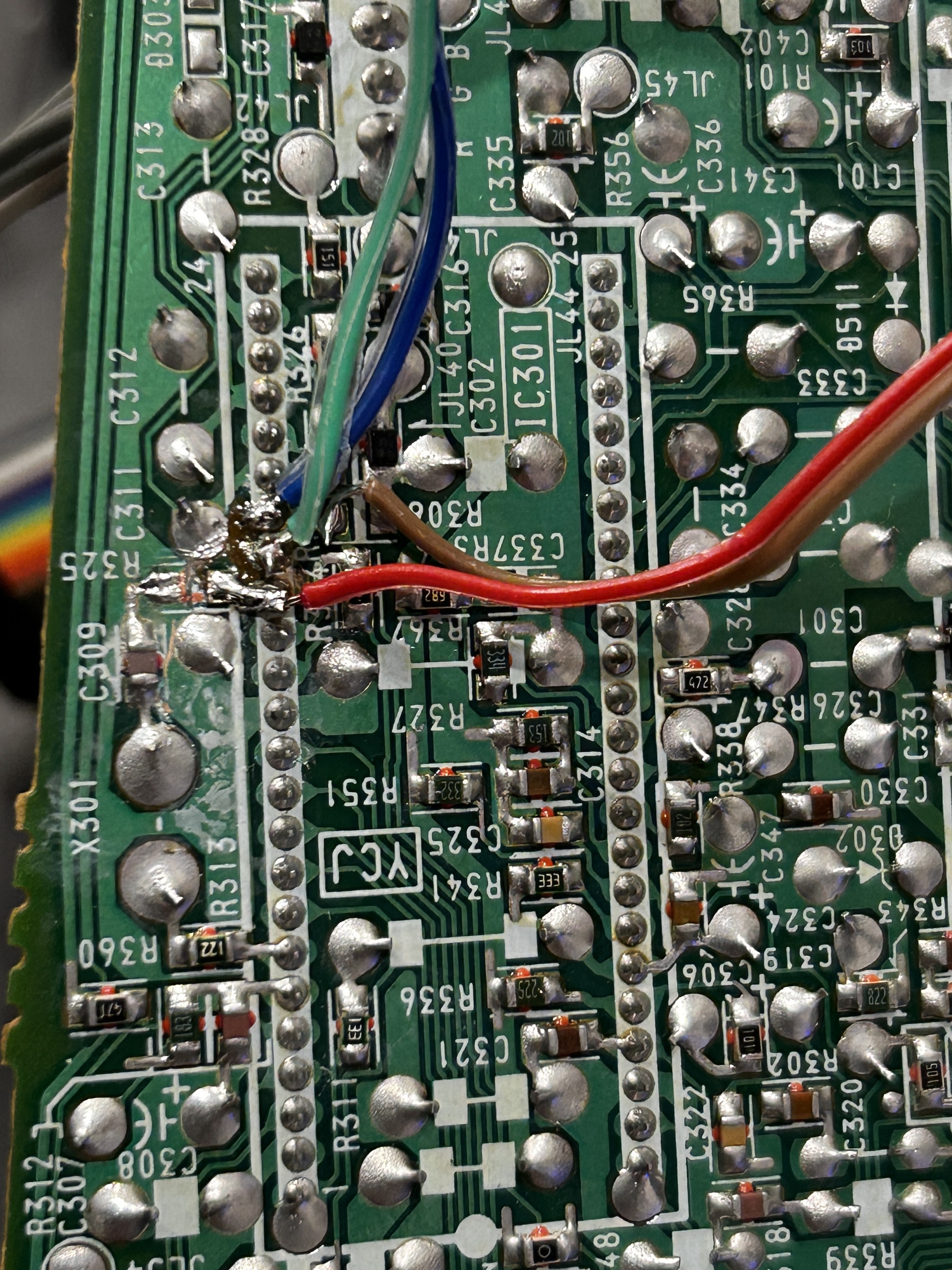
STEP 3: Connect Sync and Audio
The KV-9PT model exclusively supports mono audio. In this configuration, we will connect both the left audio (grey) and right audio (white) wires together, and directly connect them to the mono audio input. To ensure proper current and voltage delivery to the mono input, two 1kΩ resistors on the mux board will be utilized. The accompanying pictures below illustrate the wiring setup for visual reference.
The good news is that there are already ideal soldering points available for connecting these wires.
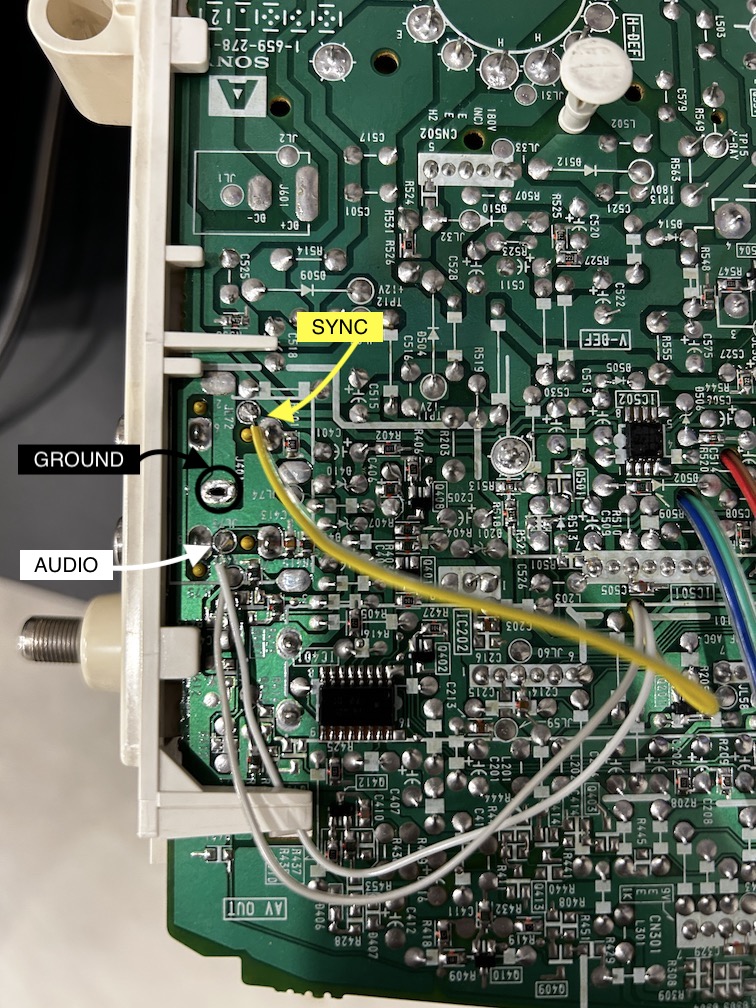
Sync wire (yellow) will be connected directly to the composite input.
To establish a common ground connection, we will connect and solder all the ground wires (black, orange, and purple) together. This consolidated ground connection will be securely soldered to one of the ground vias located near the composite input.
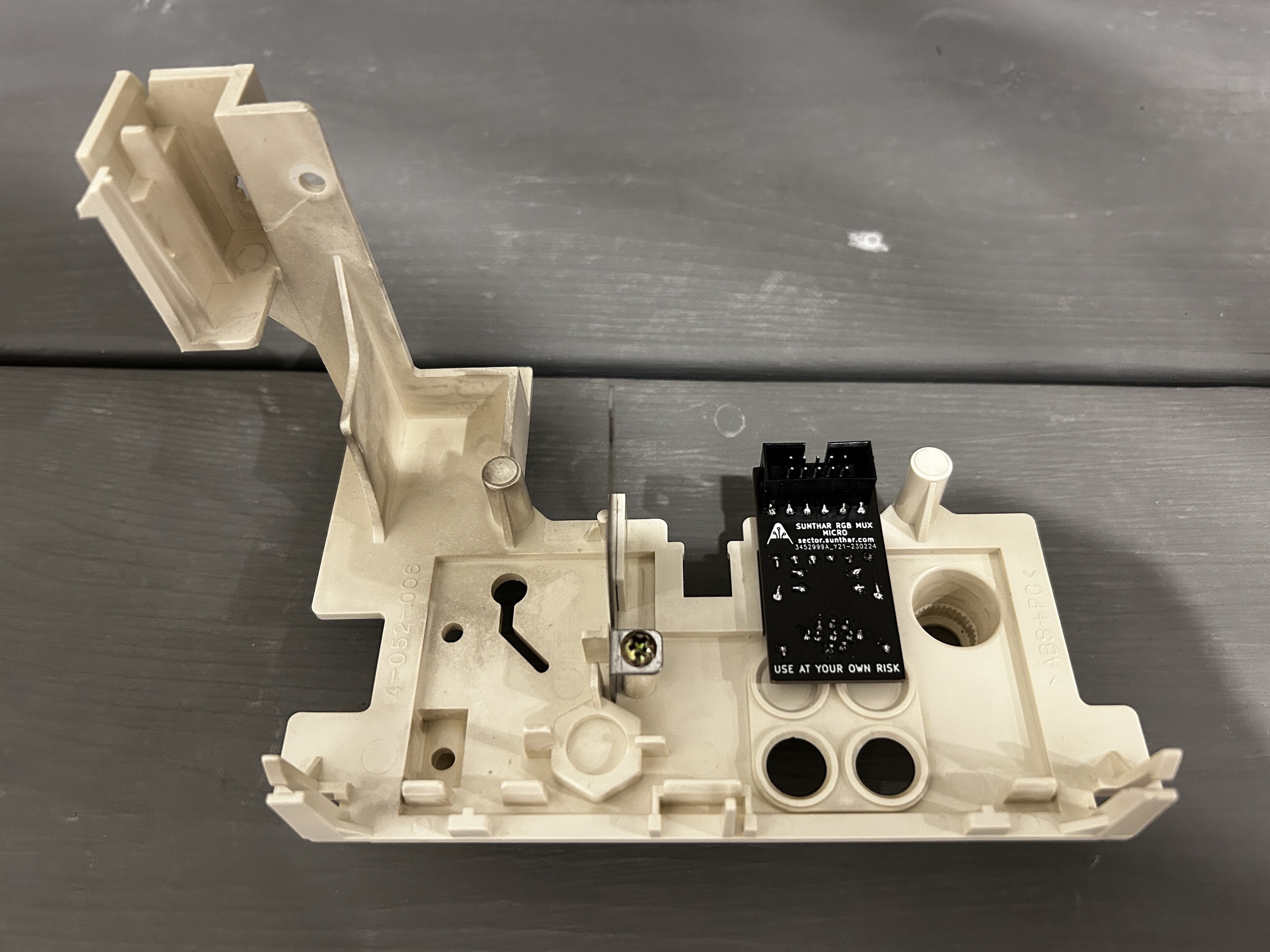
STEP 4: Build your mux board (using the micro RGB board)
Below mod uses the RGB mux board. However, it is optional for BA-1 chassis. Using the mux board makes the mod neater and easier. Please note for this mod, 0.1uF caps were used in place of R4, R5, R6 resistors.
Buy your RGB mux board with the necessary parts to complete this mod
| TV Model | KV-9PT50 |
|---|---|
| Audio LR (R7, R8) | 1kΩ |
| RGB termination (R1, R2, R3) | 75Ω |
| RGB inline caps (R4, R5, R6) | 0.1uF |
| Diode (R9) | 1N4148 |
| Blanking Resistor (R11) | 1kΩ |
Caps were used on the mux board instead of RGB inline resistors.
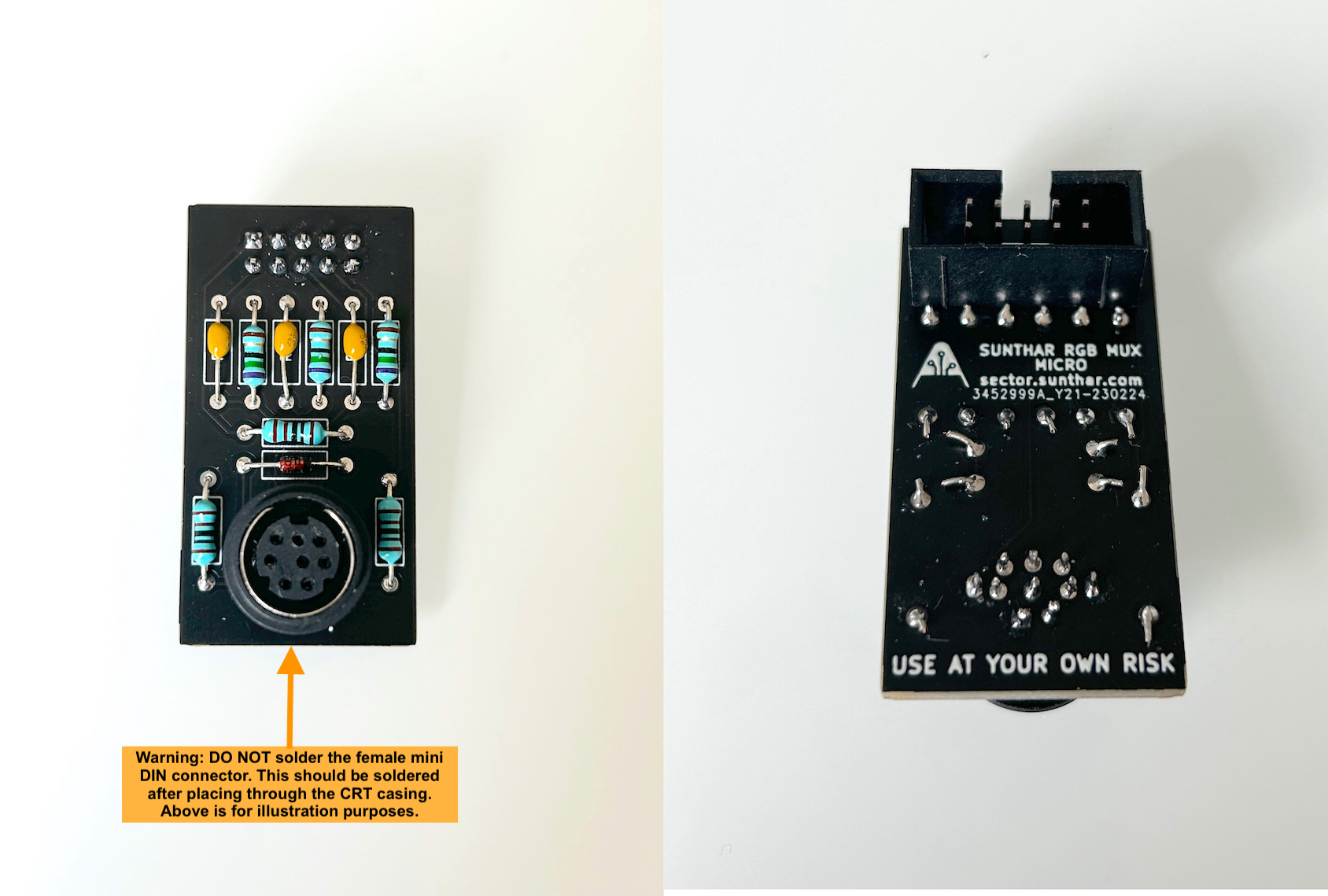

Warning
In the picture above, I'm showing the MD8 connector placed in the PCB for illustration purposes. Yet, for the practical modification, you will initially need to insert the MD8 female connector through a hole that is precisely sized to allow the body to fit through. Following this, you can solder the PCB by aligning the pins accordingly. It may be necessary to use adhesive like super glue to secure the MD8 connector in position, preventing any rotational movement. See pictures below.

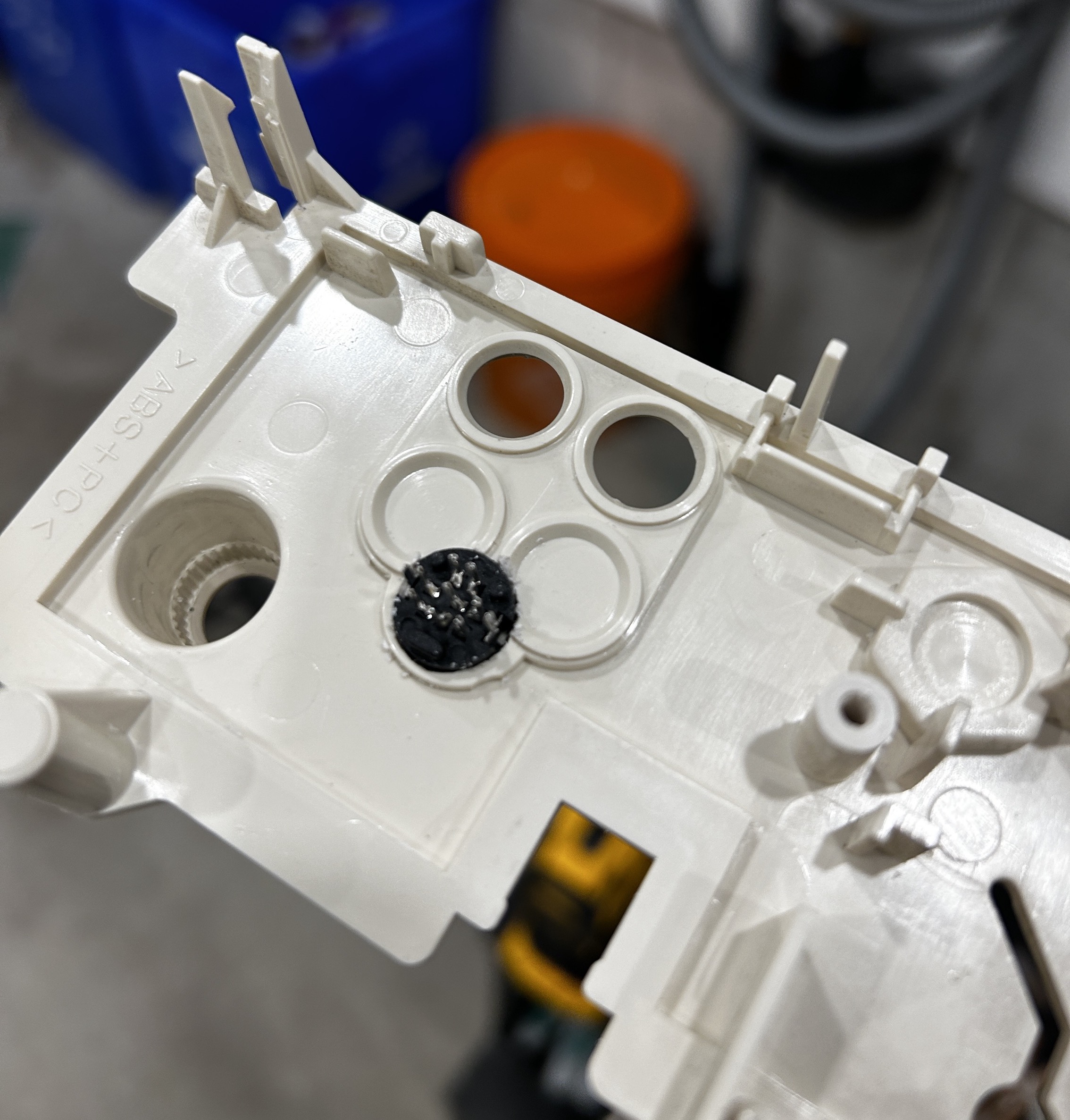
Buy your RGB mux board with the necessary parts to complete this mod
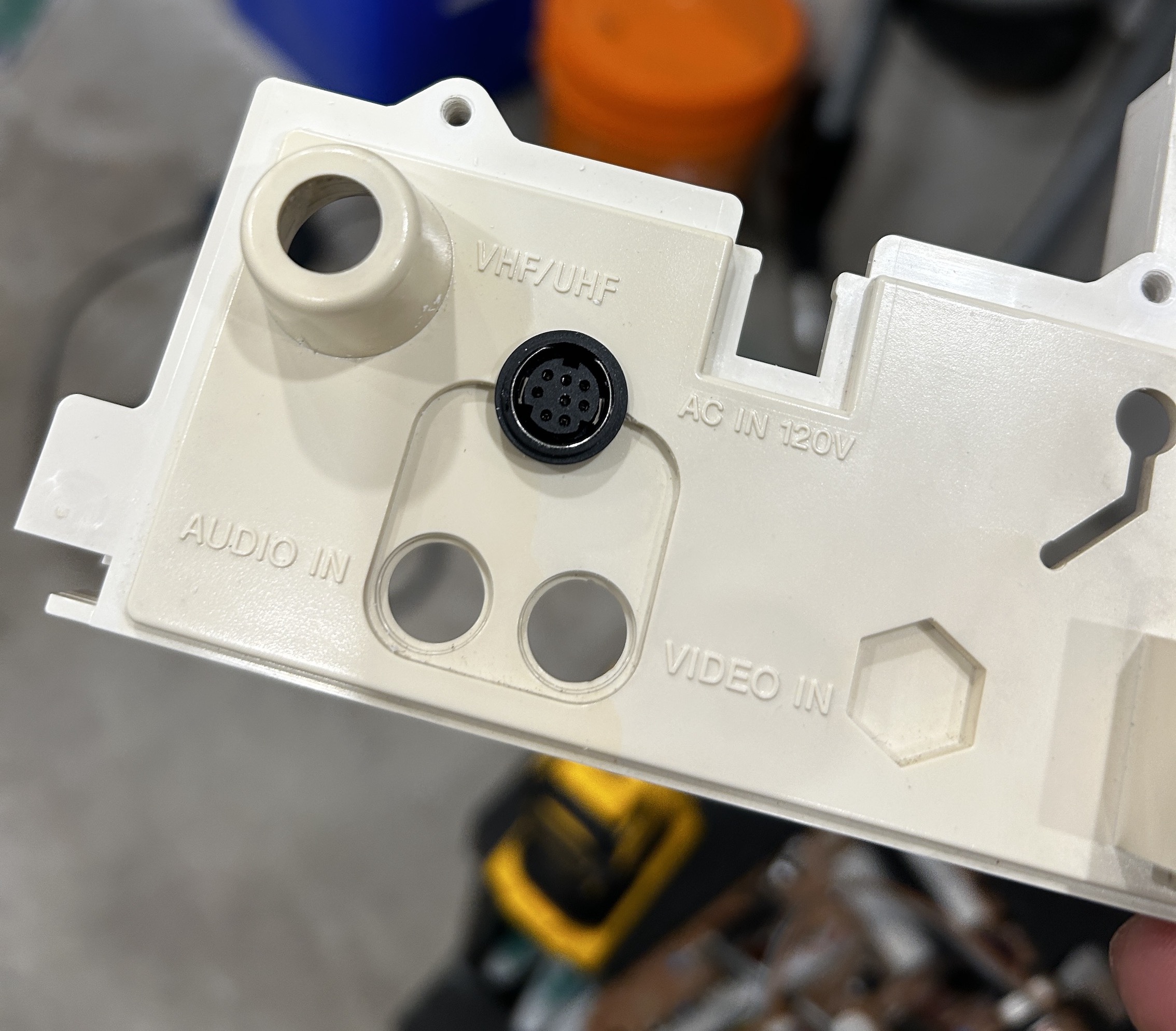
STEP 5: Attach the female SCART connector to TV
I chose the XRGB-mini port for the RGB mod here. This CRT had limited space and an RGB port needed to be carefully planned.
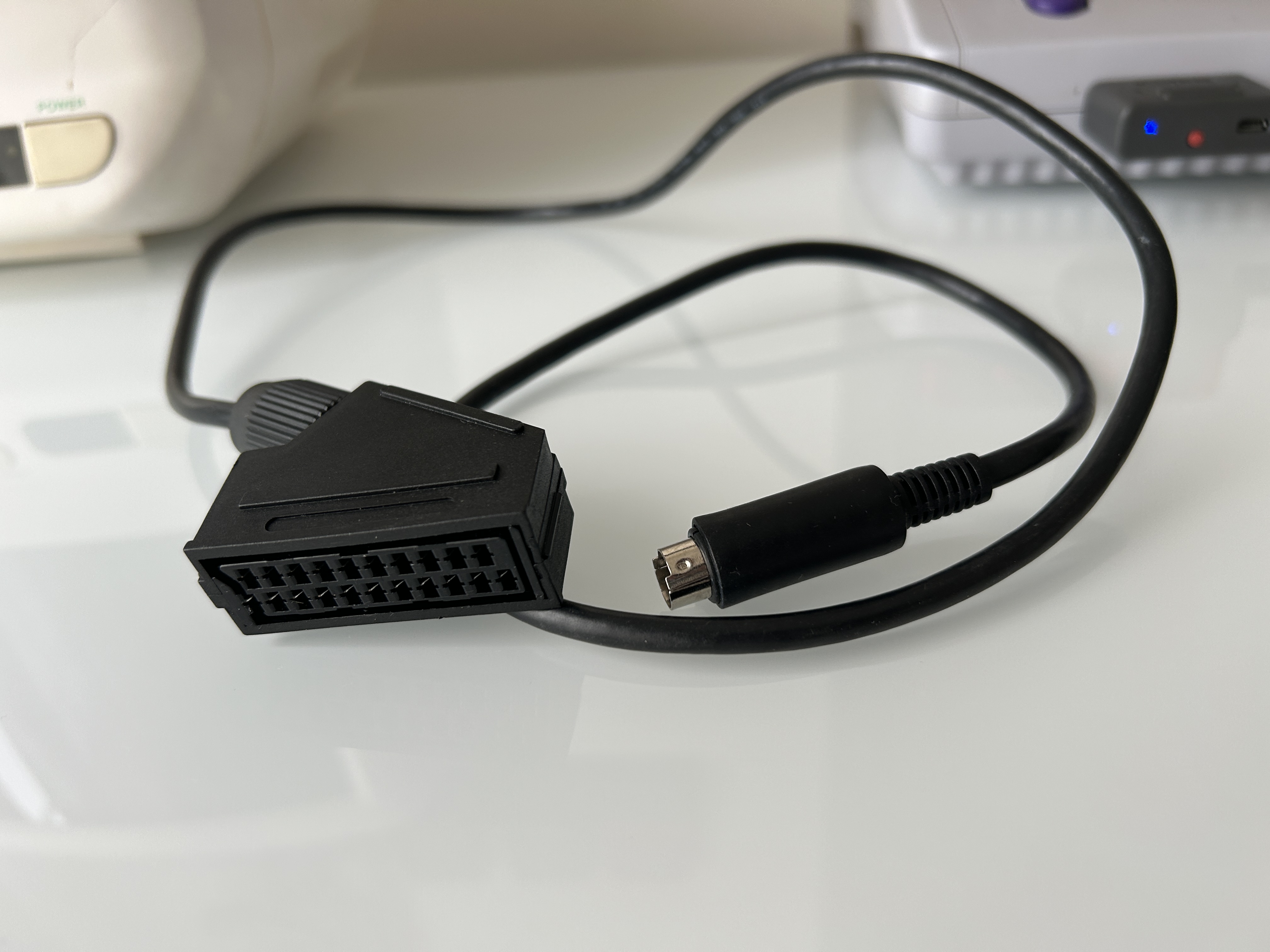
STEP 6: Make the SCART breakout cable
I'm using the XRGB-mini to SCART here. You can also use MD to SCART cable as well (which might be more readily available).
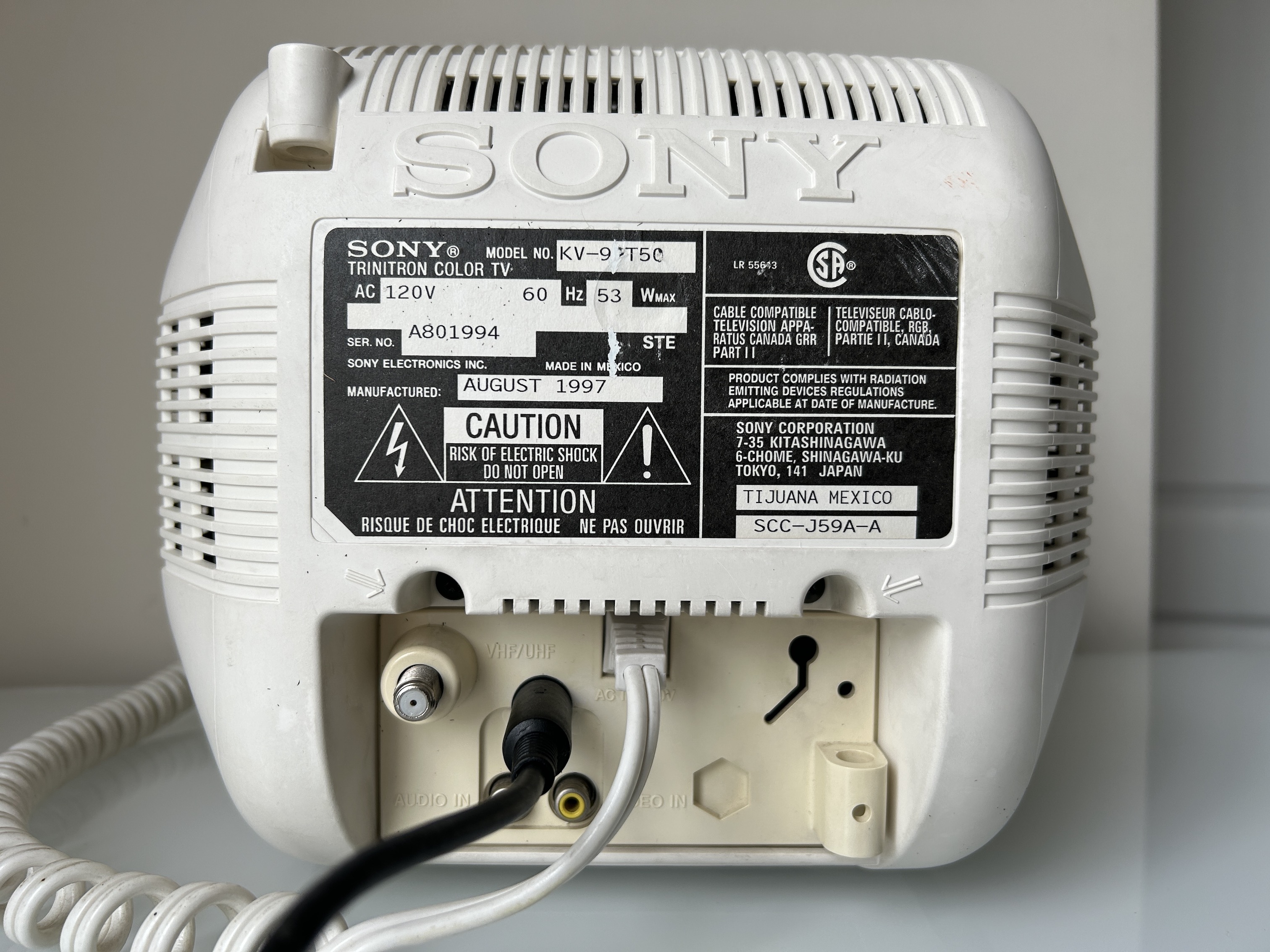


Pictures of the mod
OSD
Menu on top of the Contra III game 
Games
NES - Everdrvive Menu 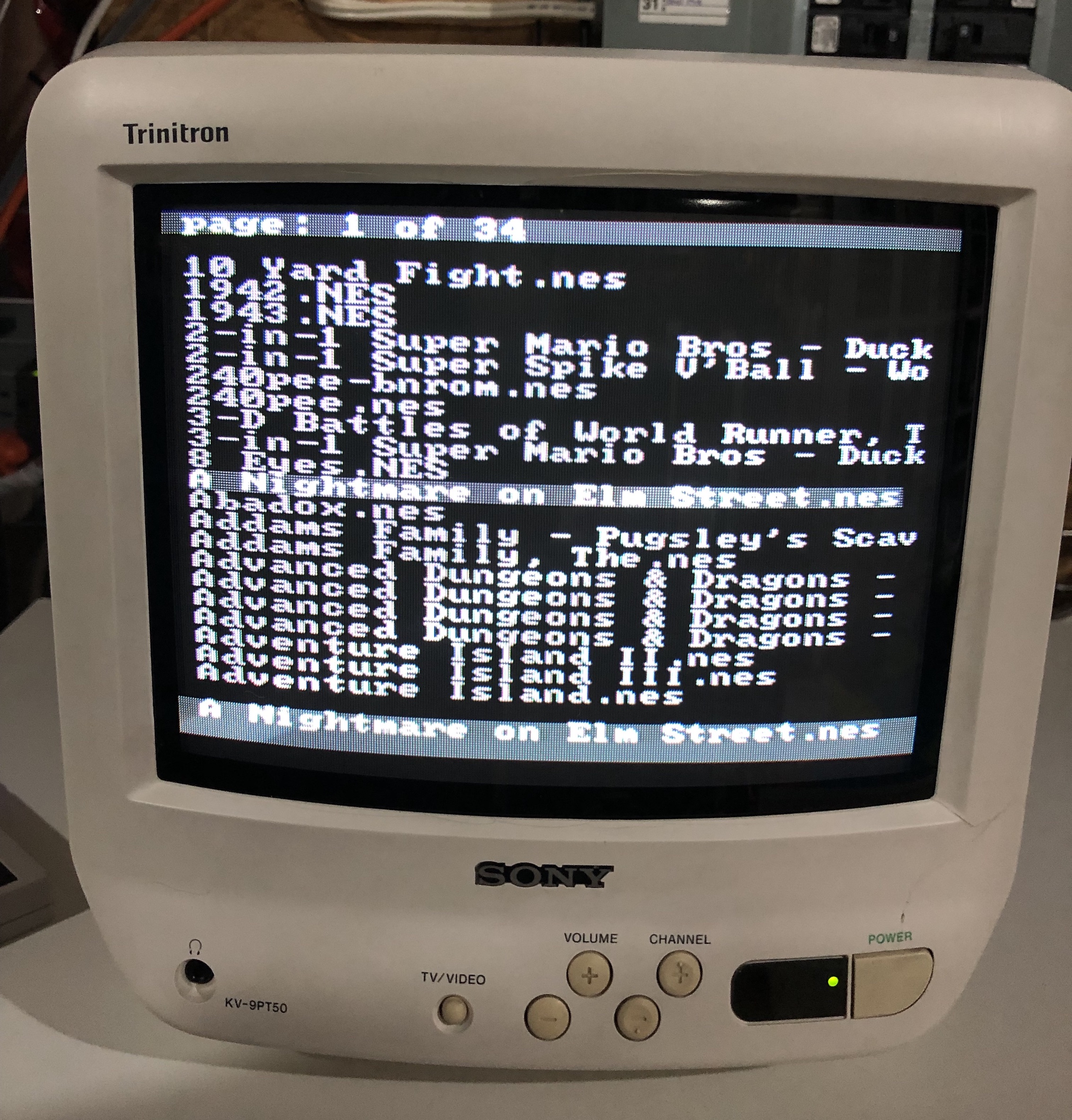
SEGA Genesis - Sonic 
SNES - Yoshi's Island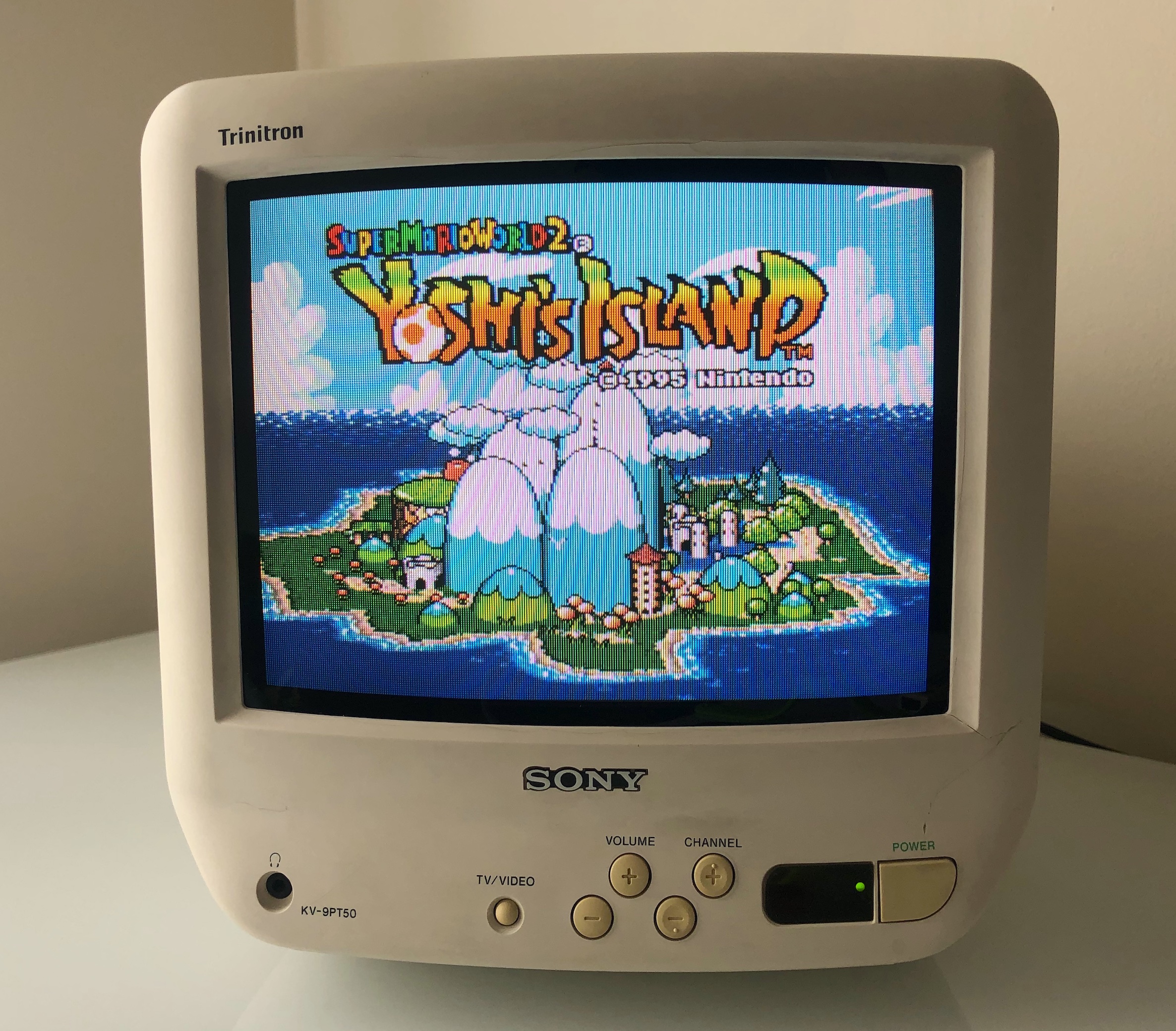 

SNES - Super Mario World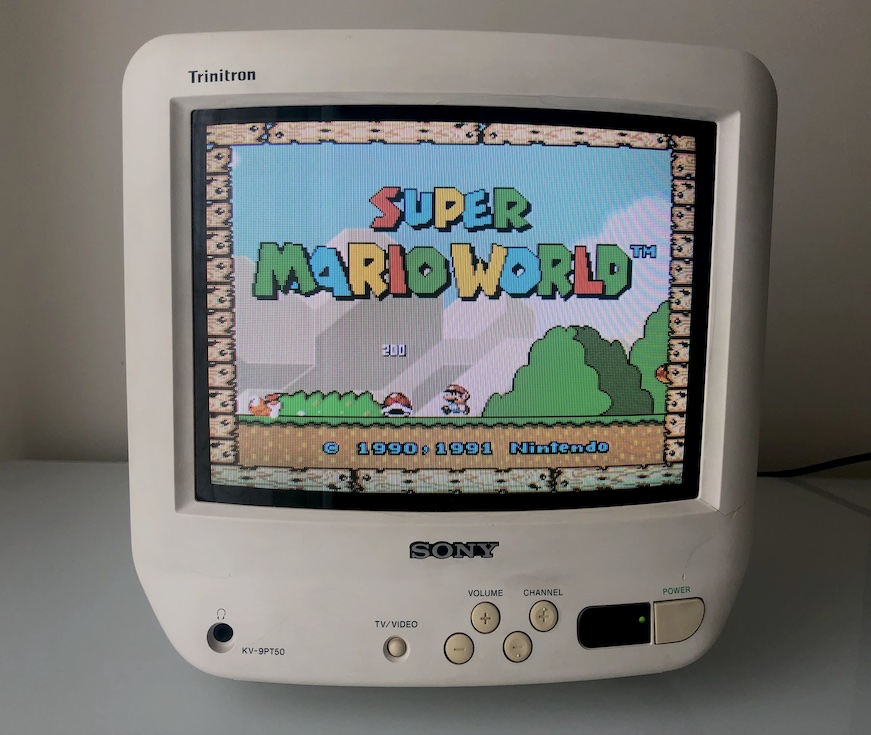 
Patterns
Grid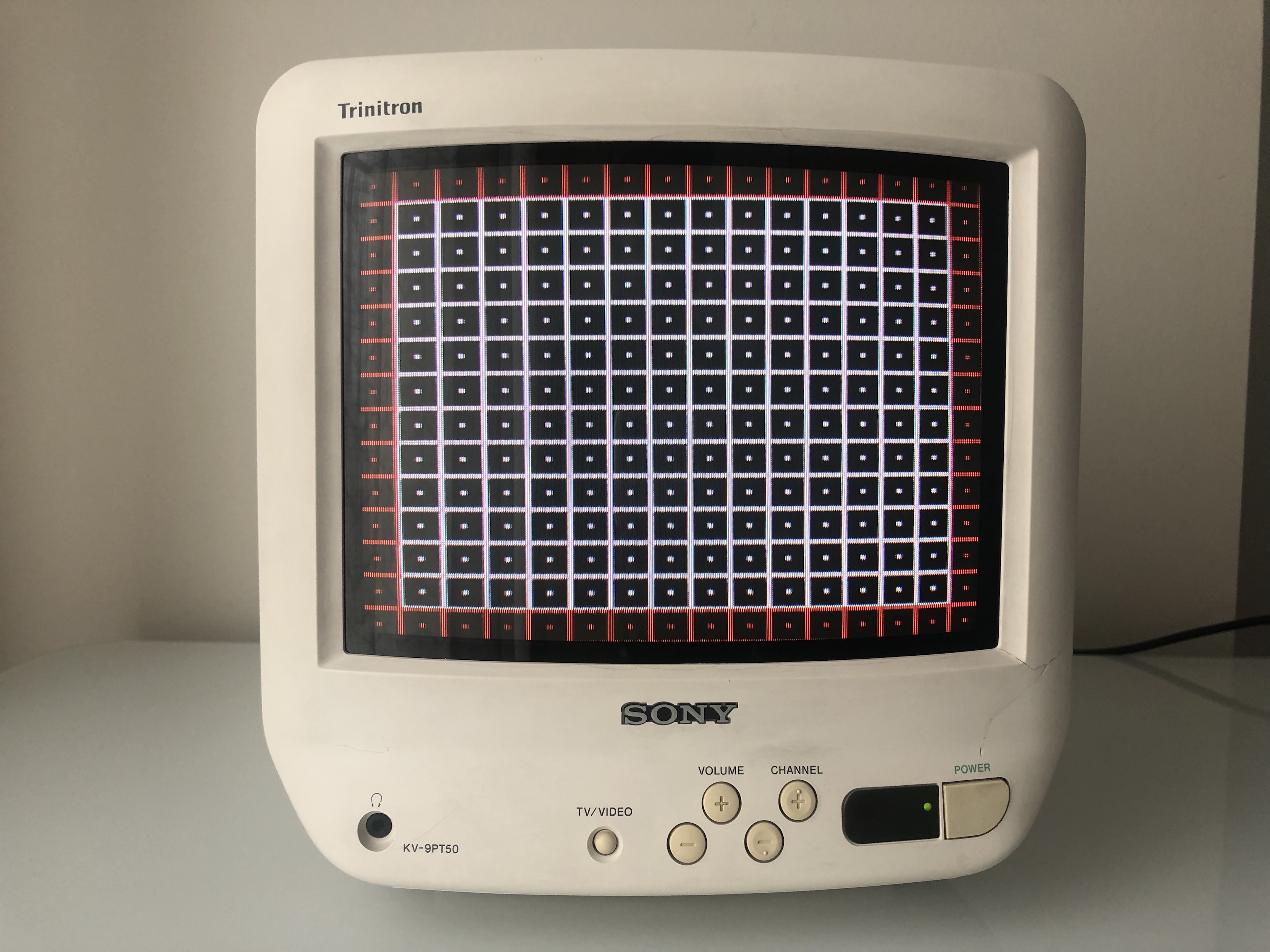 
Monoscope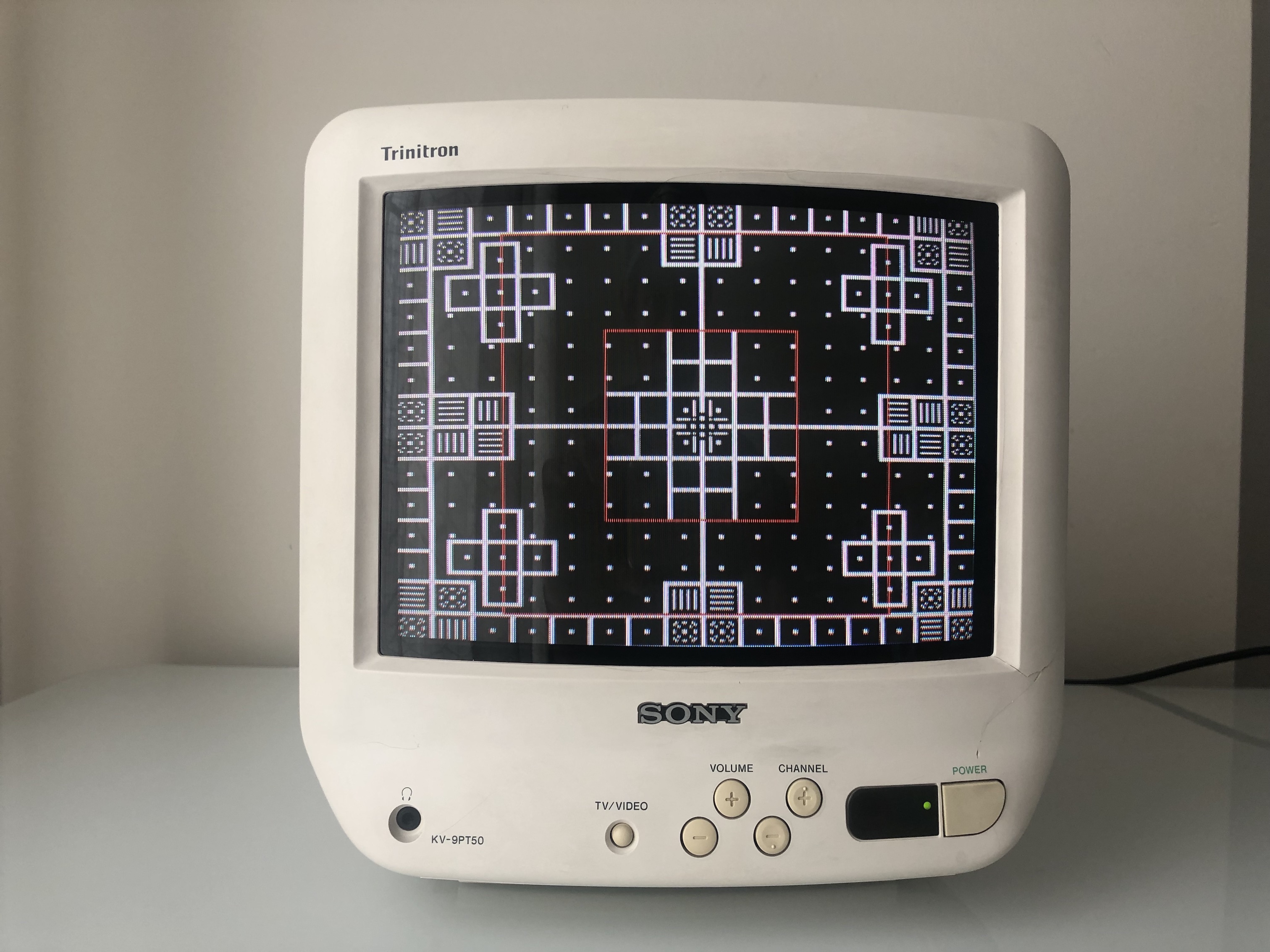 
SMPTE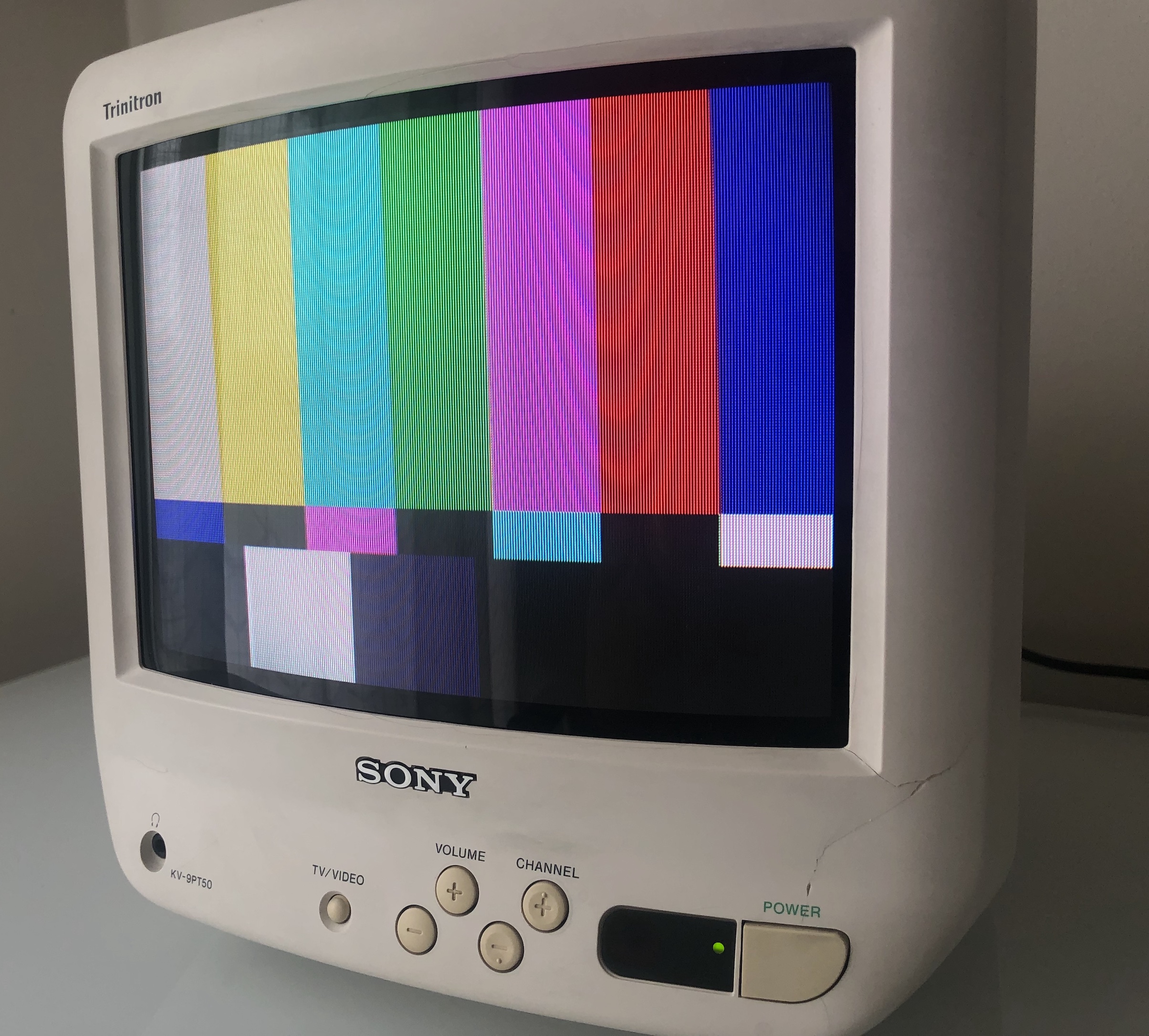 
Inside of the CRT
A board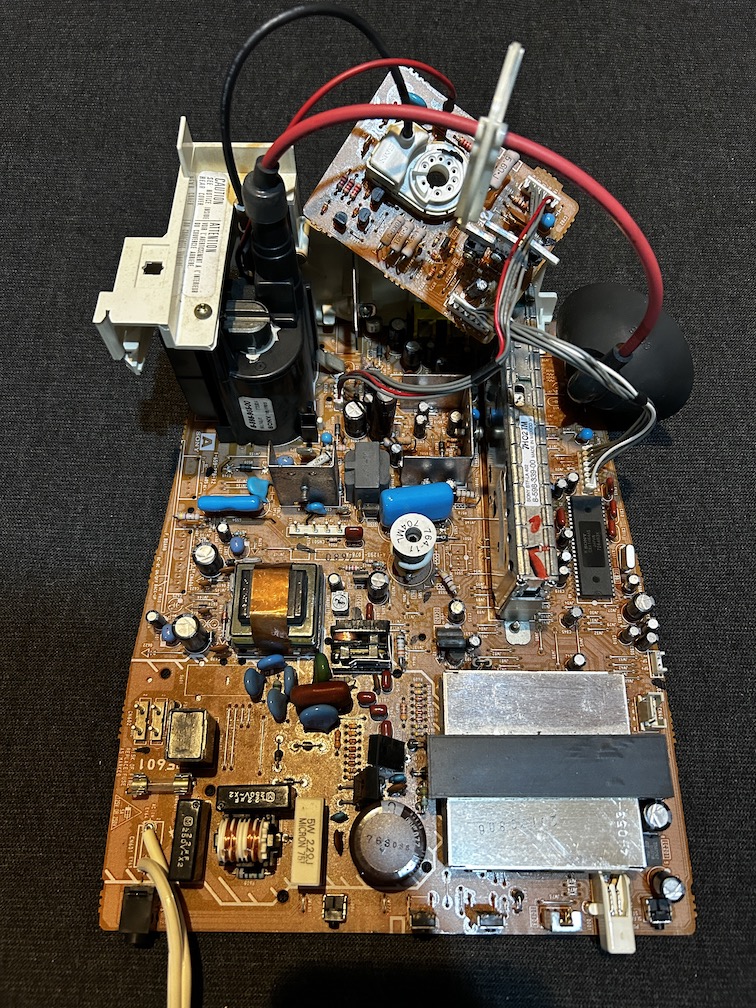 
Chroma IC 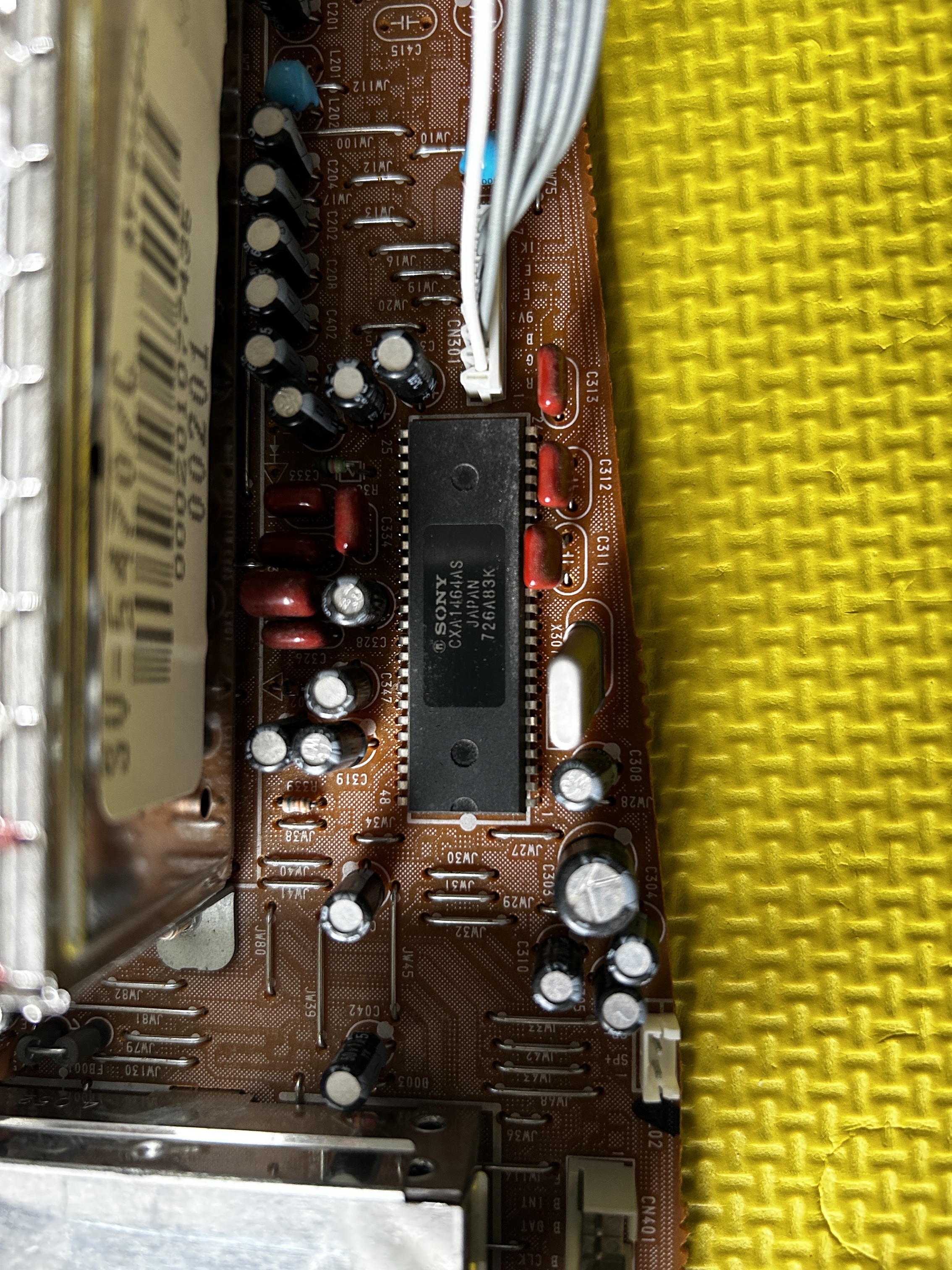
Flyback 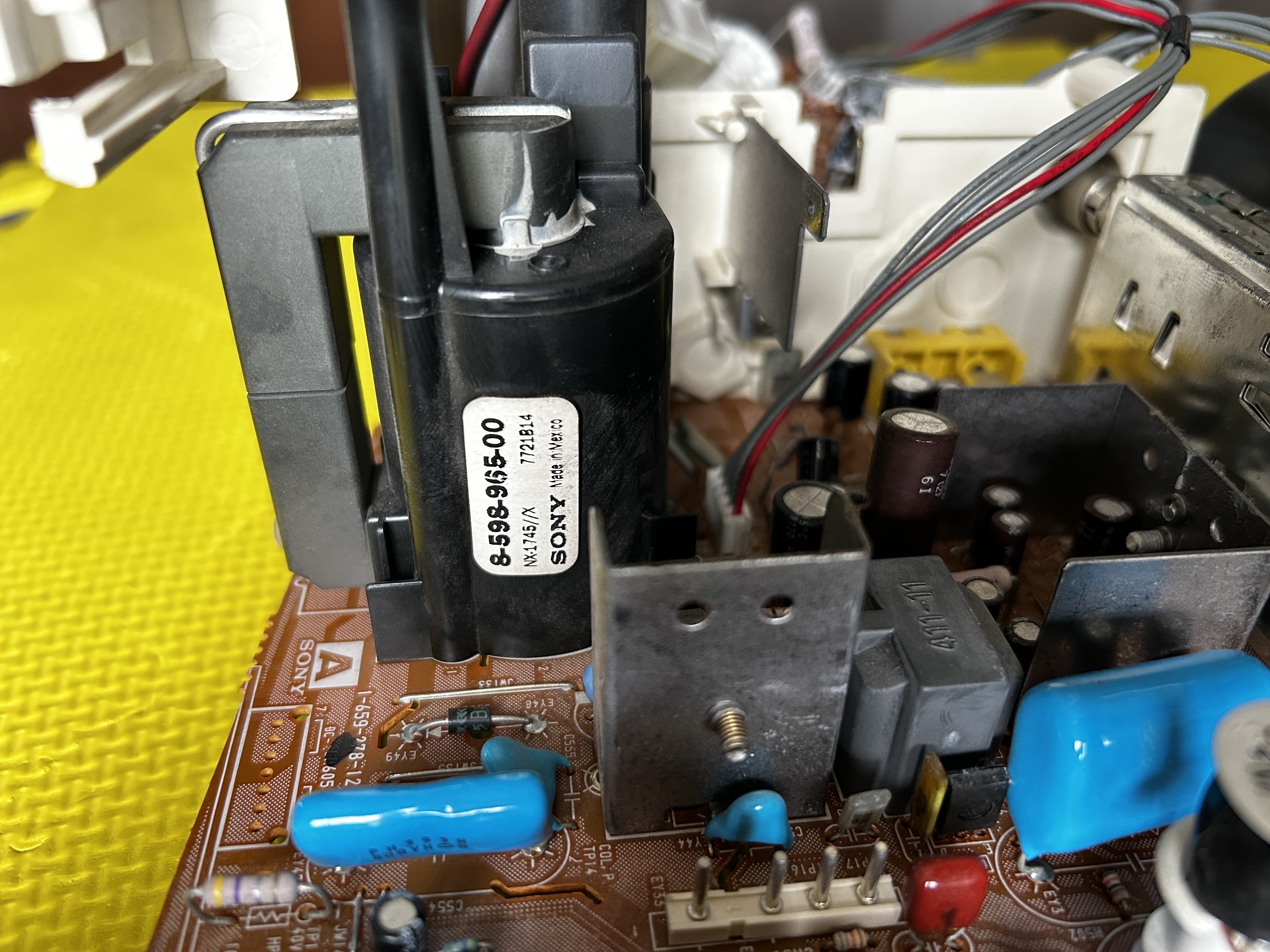
Front buttons 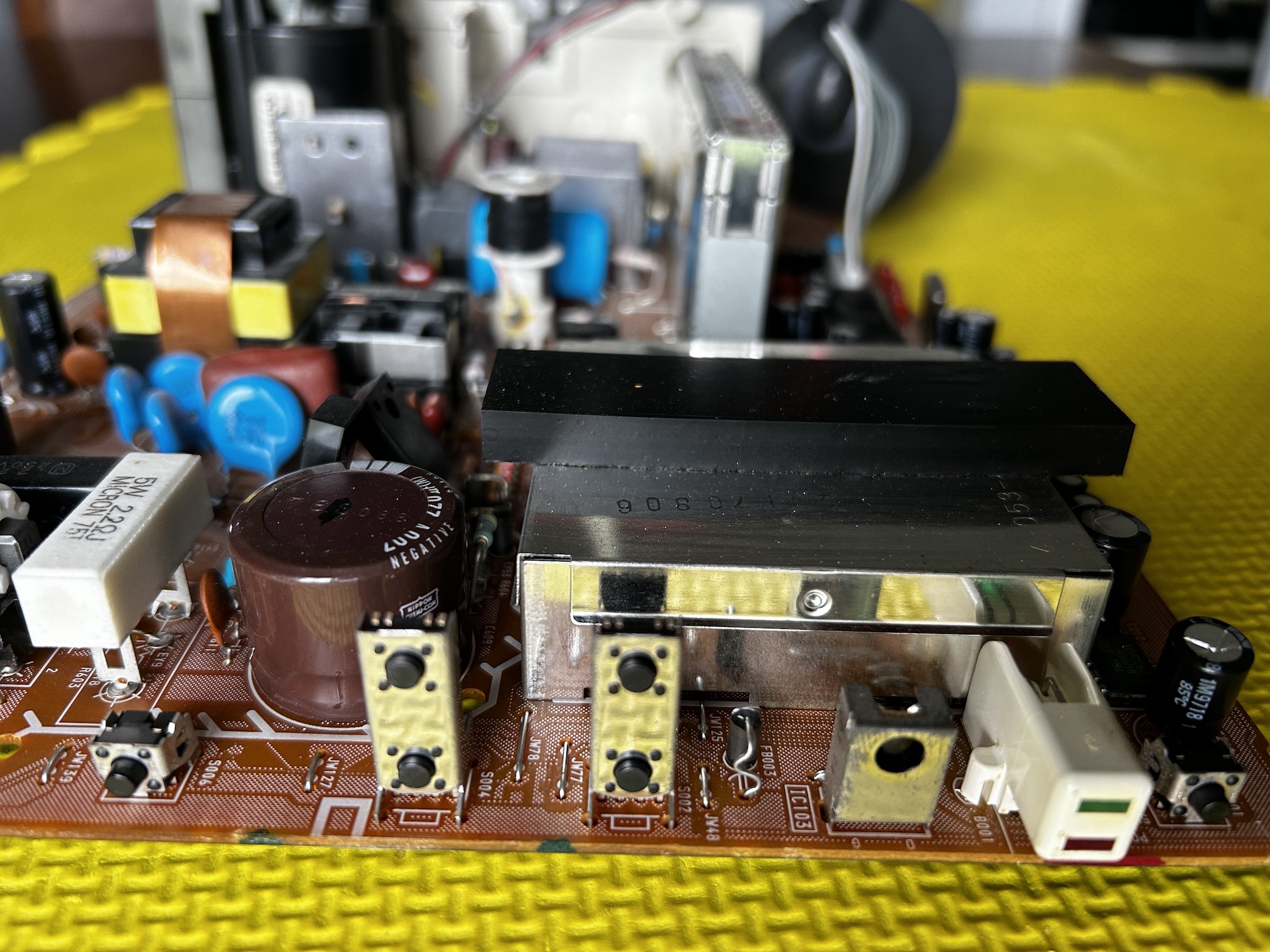
Back view 
Side view 
Top view 
Neck board 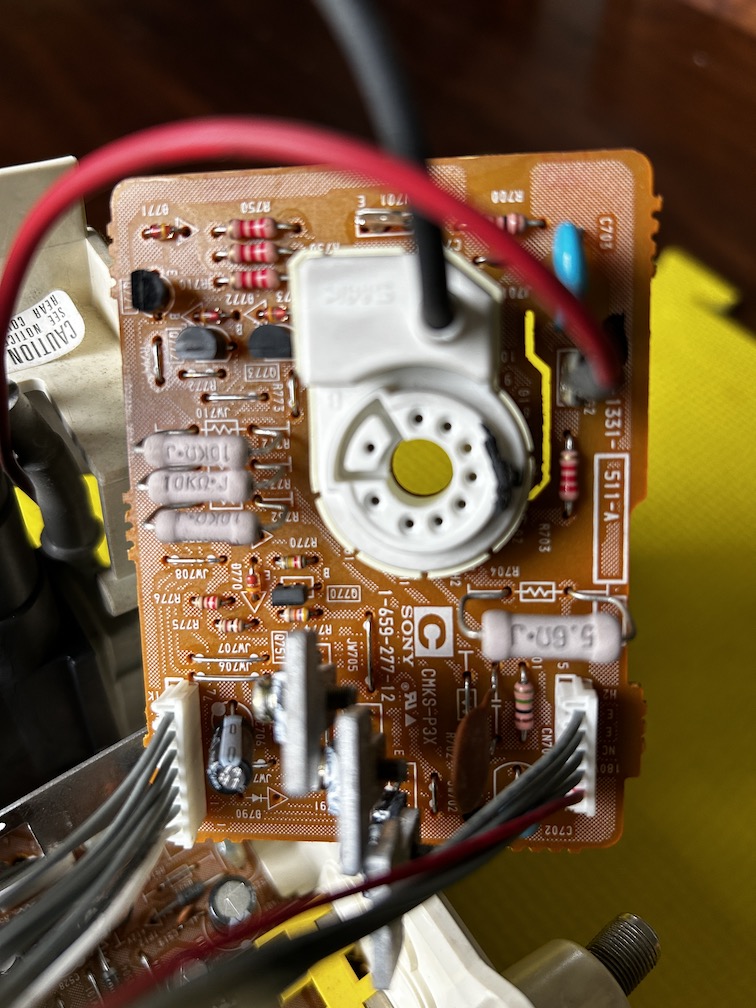
Service Menu
On the remote, press keys in this sequence DISPLAY, 5, VOL +, POWER
1 and 4 to select 3 and 6 to adjust
MUTING, ENTER to write to memory.
| NUM | SETTING | VALUE | CHANGED |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AFC | 0 | DEFAULT |
| 2 | HFRE | 71 | DEFAULT |
| 3 | VFRE | 10 | DEFAULT |
| 4 | VPOS | 20 | DEFAULT |
| 5 | VSIZ | 35 | DEFAULT |
| 6 | VLIN | 7 | DEFAULT |
| 7 | VSCO | 4 | DEFAULT |
| 8 | HPOS | 14 | 12 |
| 9 | HSIZ | 14 | DEFAULT |
| 10 | PAMP | 15 | DEFAULT |
| 11 | CPIN | 4 | DEFAULT |
| 12 | PPHA | 7 | DEFAULT |
| 13 | VOM | 2 | DEFAULT |
| 14 | GAMP | 11 | DEFAULT |
| 15 | BAMP | 9 | DEFAULT |
| 16 | GCUT | 9 | DEFAULT |
| 17 | BCUT | 10 | DEFAULT |
| 18 | CROM | 30 | DEFAULT |
| 19 | SPIX | 15 | DEFAULT |
| 20 | SHUE | 26 | DEFAULT |
| 21 | SCOL | 29 | DEFAULT |
| 22 | SBRT | 35 | 33 |
| 23 | RGBP | 31 | DEFAULT |
| 24 | SHAP | 9 | DEFAULT |
| 25 | VSMO | 0 | DEFAULT |
| 26 | REF | 1 | DEFAULT |
| 27 | ROFF | 1 | DEFAULT |
| 28 | GOFF | 1 | DEFAULT |
| 29 | BOFF | 1 | DEFAULT |
| 30 | ABLM | 0 | DEFAULT |
| 31 | NOTC | 0 | DEFAULT |
| 32 | DRGB | 0 | DEFAULT |
| 33 | DISP | 7 | DEFAULT |
| 34 | SPOT | 8 | DEFAULT |
| 35 | PBLK | 13 | DEFAULT |