Sony KV (BA-4D) 27S42 RGB
Sony KV-27S42 RGB (Advanced Mod)
This advanced mod tutorial is divided into three chapters, focusing on advanced modifications to address previous challenges:
- Chapter 1: Addresses key challenges like requiring a dummy plug for stereo audio and a dummy S-Video plug to activate S-Video by grounding the detect pin.
- Chapter 2: Explores how to use a remote control to seamlessly switch between RGB, composite, and component inputs.
- Chapter 3: Demonstrates how to utilize an external blanking signal, including lower-voltage signals from MiSTer, to switch inputs automatically. This allows all stock inputs to remain functional without requiring physical switches.
Chapter 2 & 3 is in progress.

CRT safety
Caution
You can die doing this! So read carefully! CRT TV is not a toy. Do not open a CRT TV. If you don't have any prior knowledge about handling high voltage devices, this guide is not for you. CRT TV contains high enough voltage (20,000+ V) and current to be deadly, even when it is turned off.
Plan of attack
Theory
Sometimes it is nice to know the theory behind the mod. I have put this on a separate page. This shows how the various resistor values are calculated.
Service manuals
Specs
Sony KV-27S42
- Manufactured: September 1999, Mexico
- NTSC, 60 Hz - 90W
- Chassis: BA-4D
- Tube: A68LML50X
- Jungle Chip: CXA2133S/CXA2133BS
- OSD Chip: M37273MF-255SP/M37273MFH-052SP
Schematics
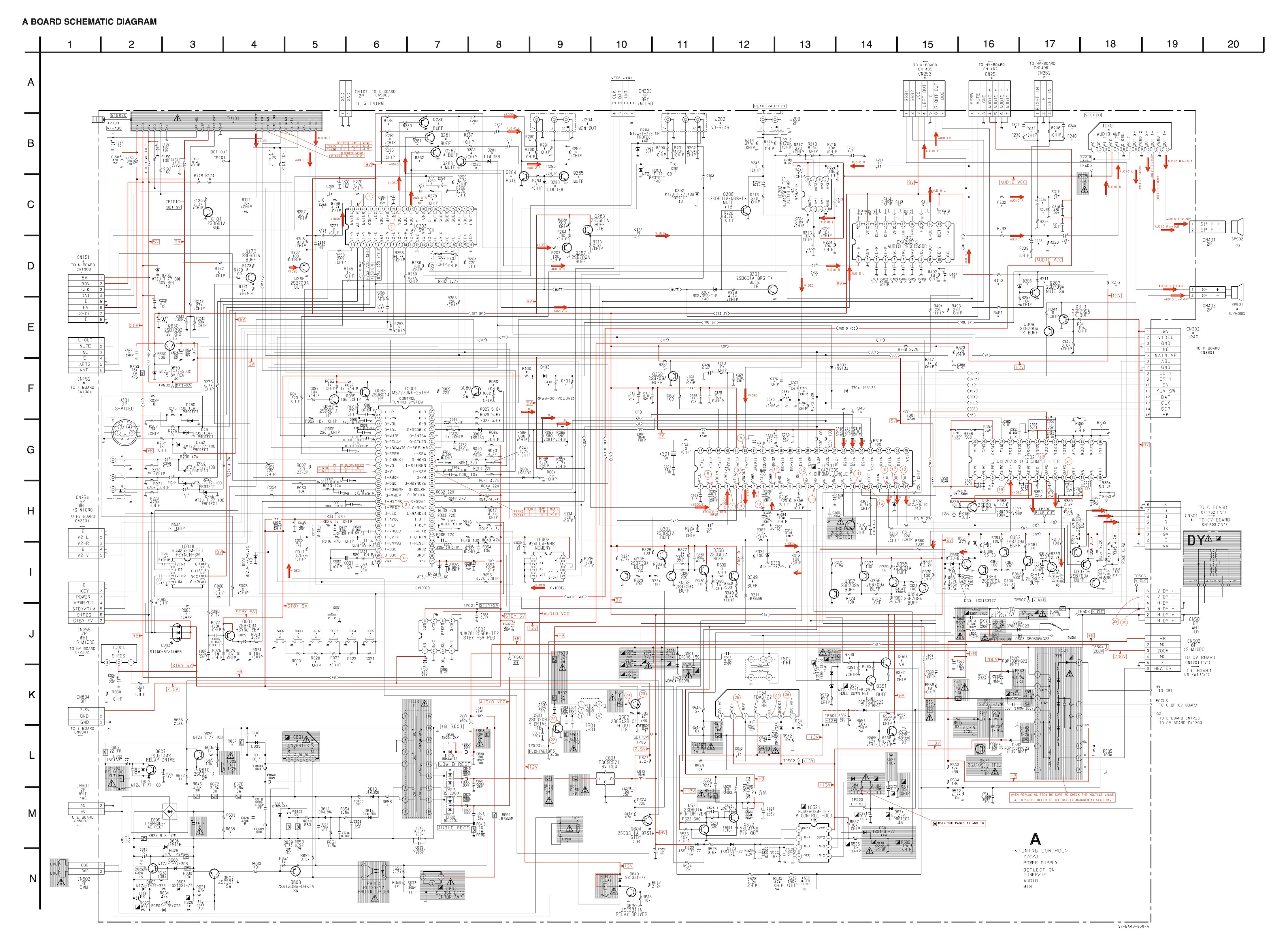
Chapter 1: No more dummy plug needed
We'll be using the diagram below for this modification. While it’s specifically designed for the KV-27S42, it is also compatible with the KV-27V42 and other 27" BA-4D chassis models that use luma for sync. However, this method does not apply to 20" or smaller BA-4D models, as they do not require luma for sync.
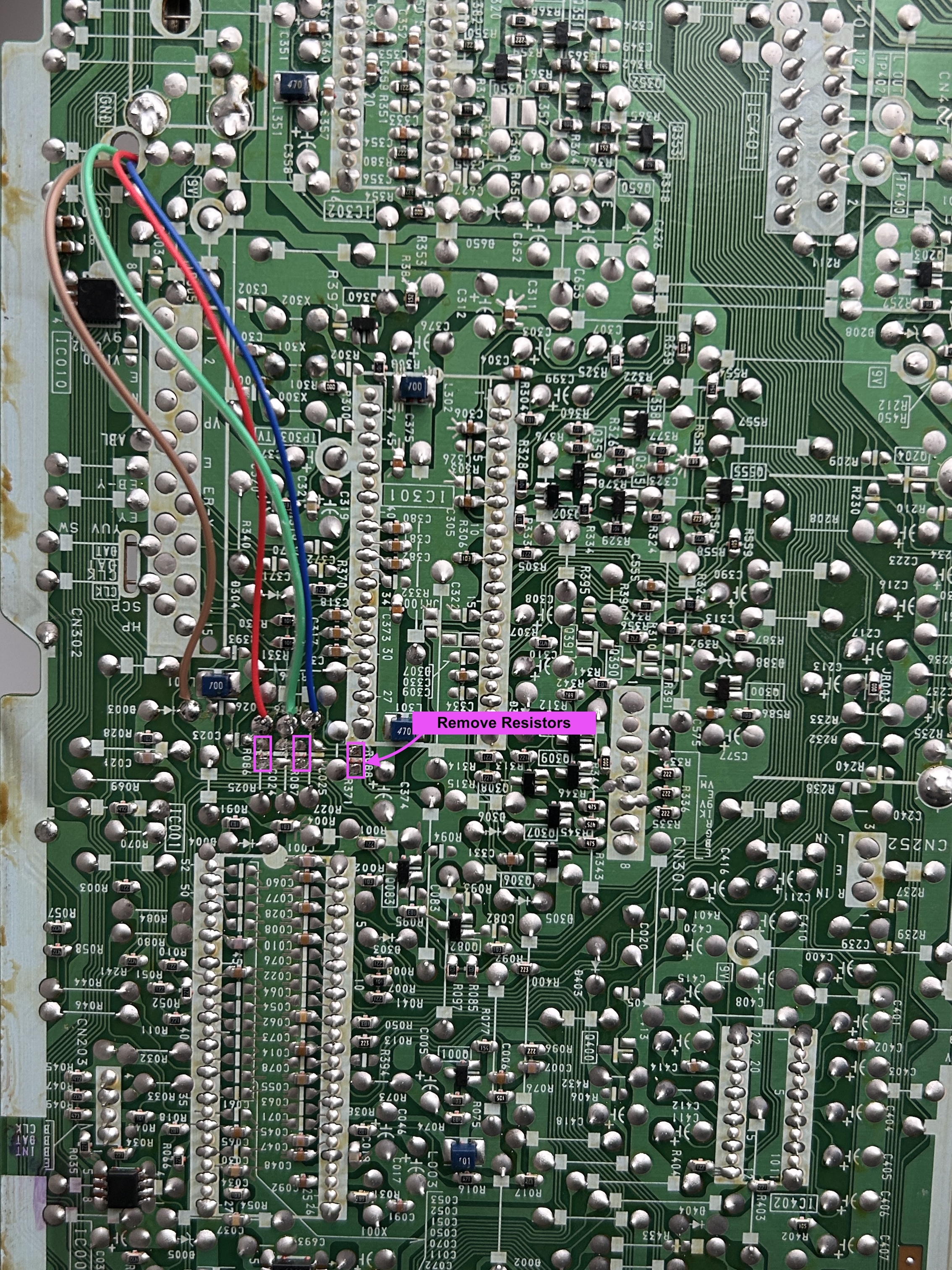
STEP 1: Remove RGB ground resistors
First we will remove the following components. So, nothing new here.
Remove the following components. RGB resistors to the ground. Please always measure and mark them, so that you know you are removing the correct partrs.
- R086 (680Ω) Red ground resistor
- R087 (680Ω) Green ground resistor
- R088 (680Ω) Blue ground resistor
STEP 2: Add RGB inline diodes
To reduce interference, it is recommended to add these inline diodes. You will be lifting one side of the R025, R026, R027 and add diodes.
Pay attention to what side the diode is added and the direction of the diode stripe.
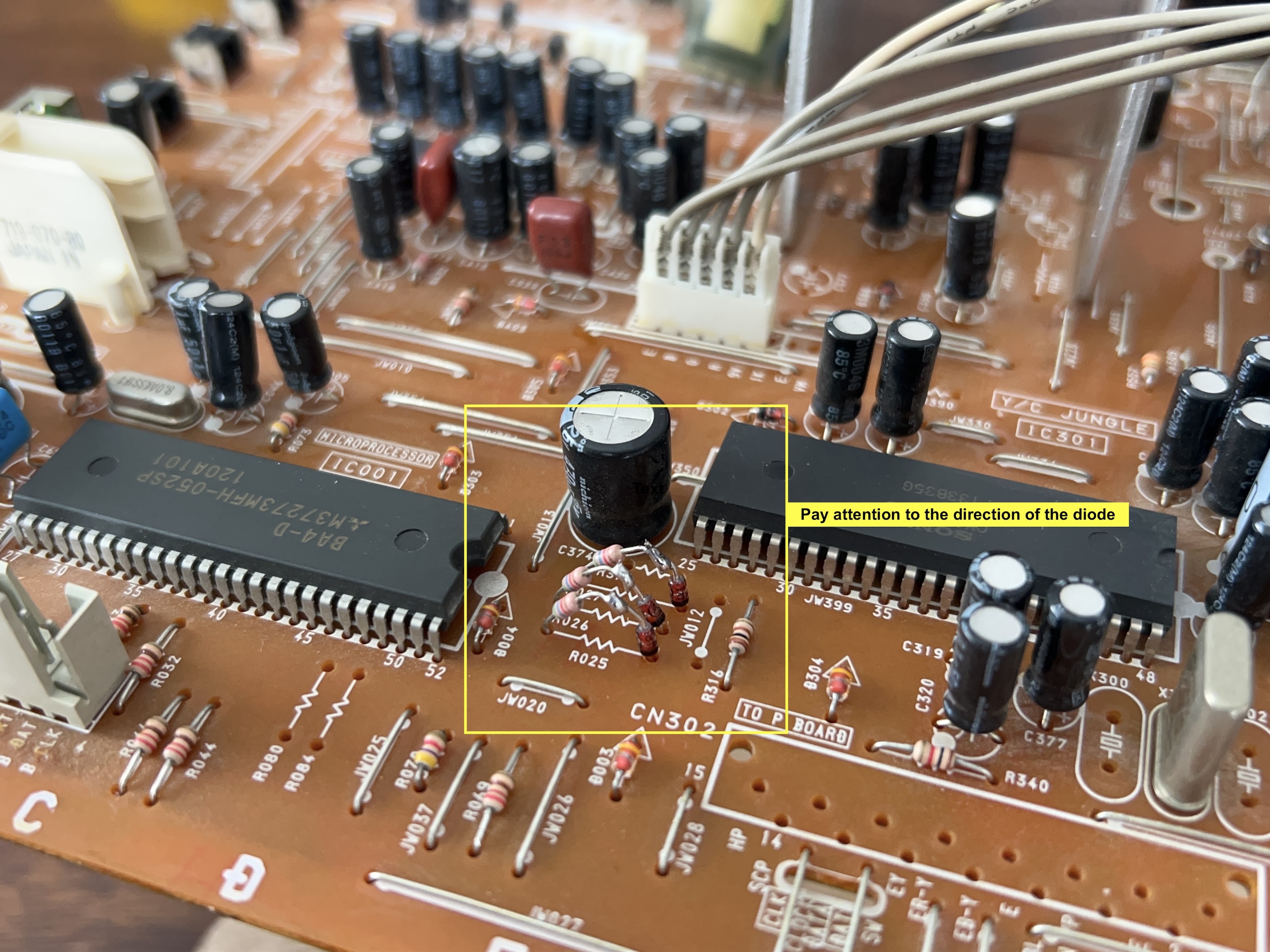
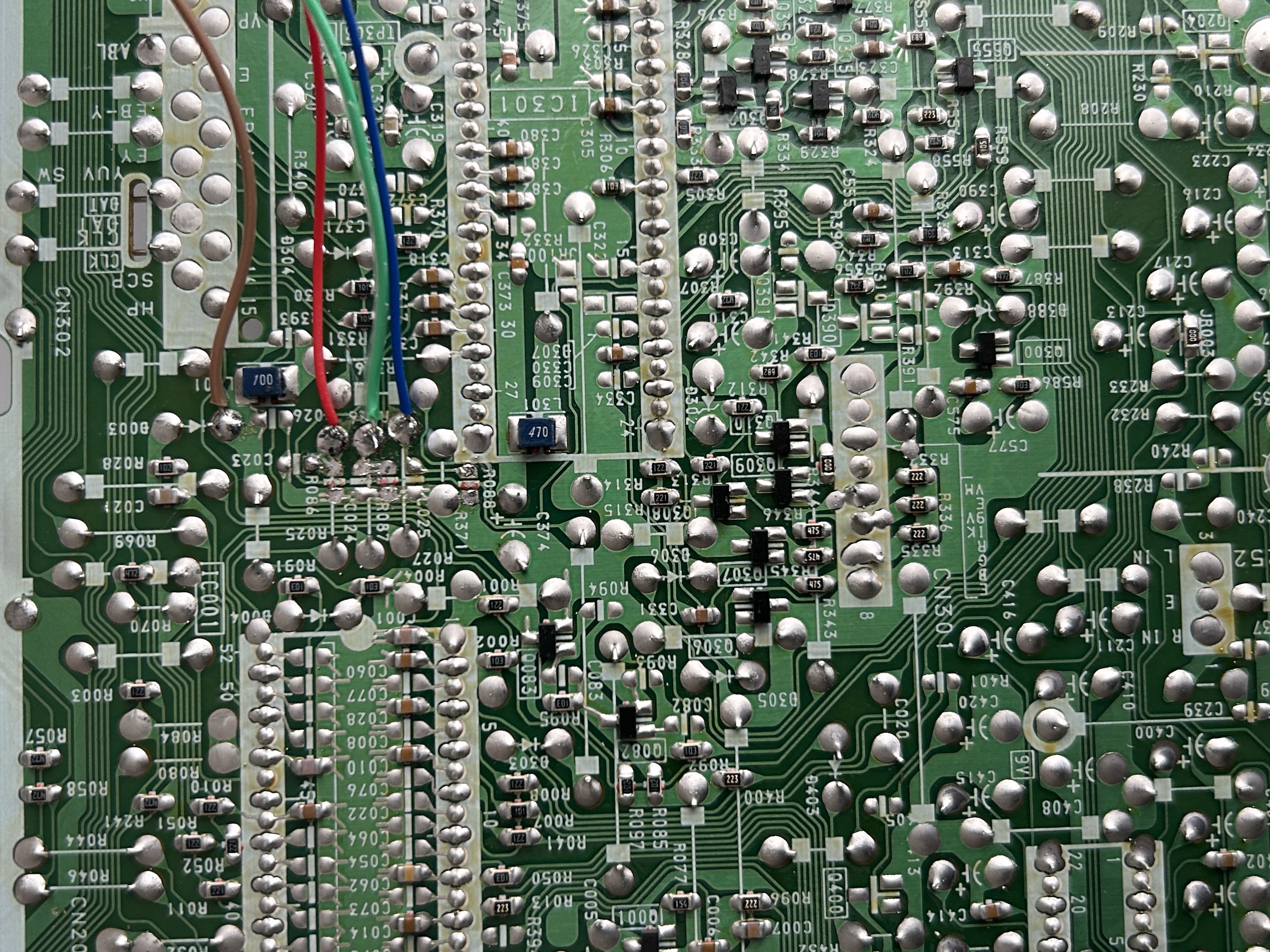
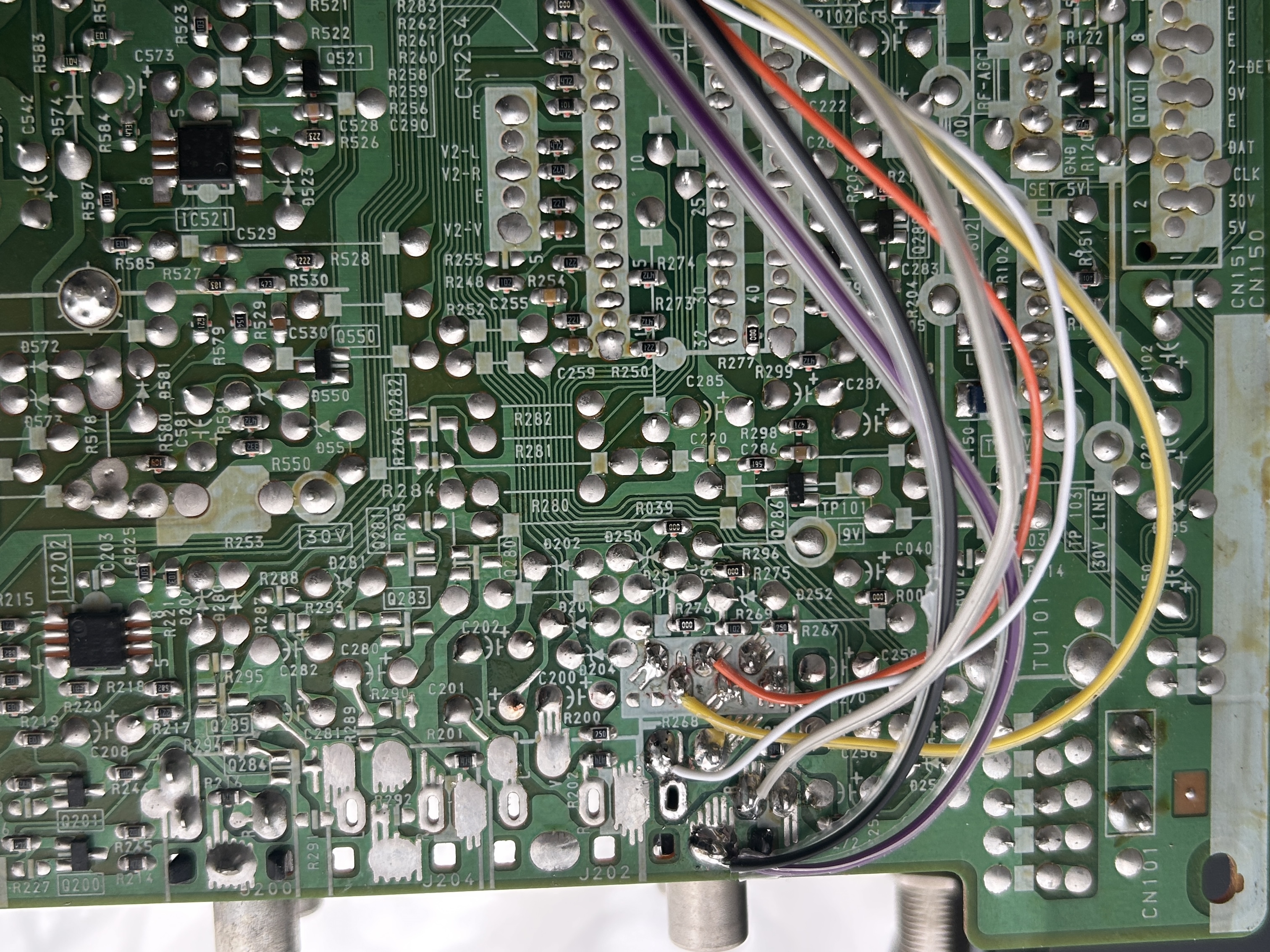
STEP 3: Attach R, G, B and blanking wires
Ensure that the R, G, B, and blanking wires are connected as shown in the picture.
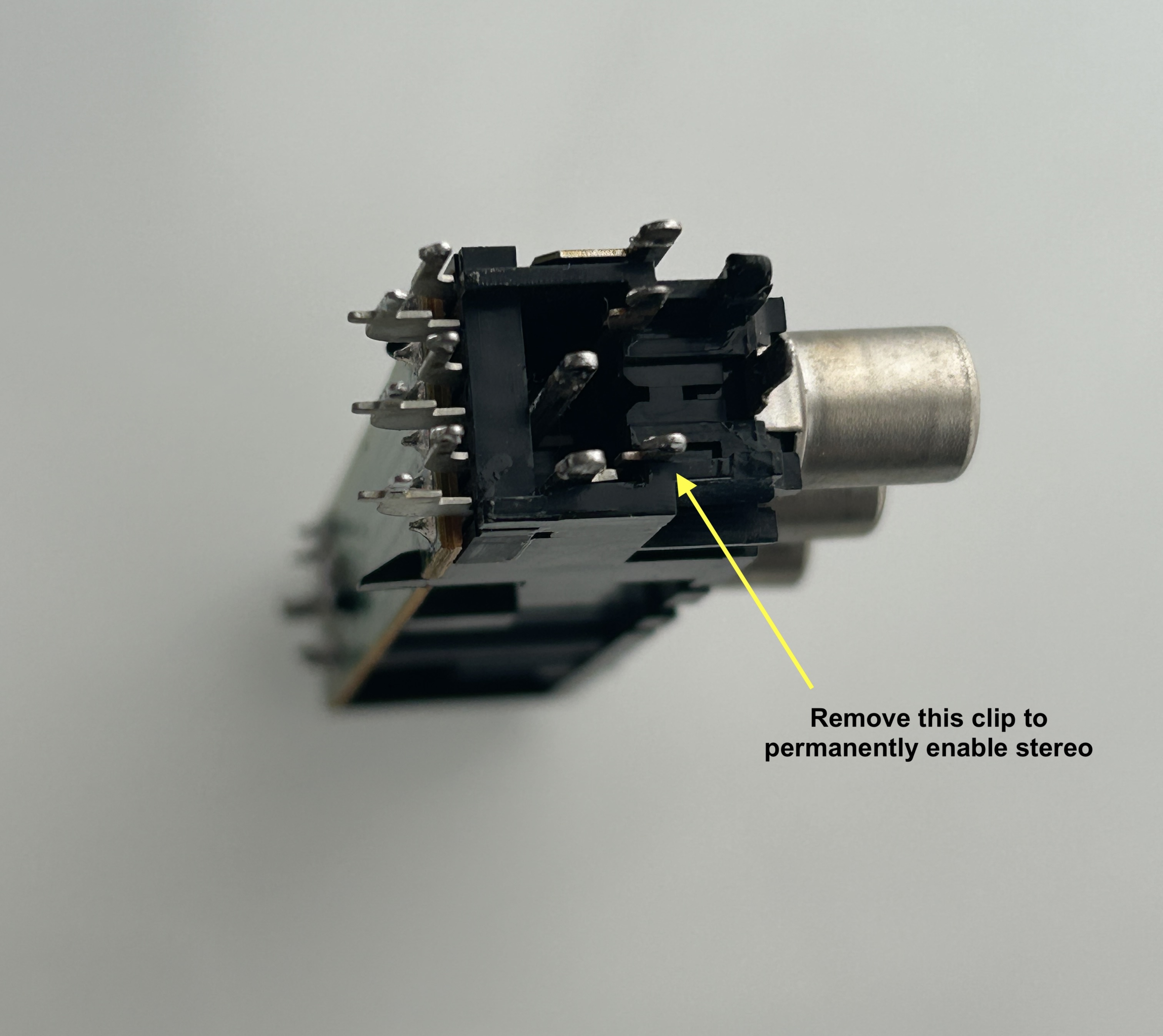
STEP 4: Permanently enable stereo
Permanently enabling stereo can be a bit tricky, especially if you're using Video 1 input sync for RGB. Here are your options:
- Option 1 (Recommended): Simply insert a plug into the red RCA port. This is the easiest and most effective method.
- Option 2 (Not Recommended): Cut the trace to force stereo. However, this isn't as simple as a single cut—you'll need to cut the trace from both sides and then resolder the right audio connection back into the circuit.
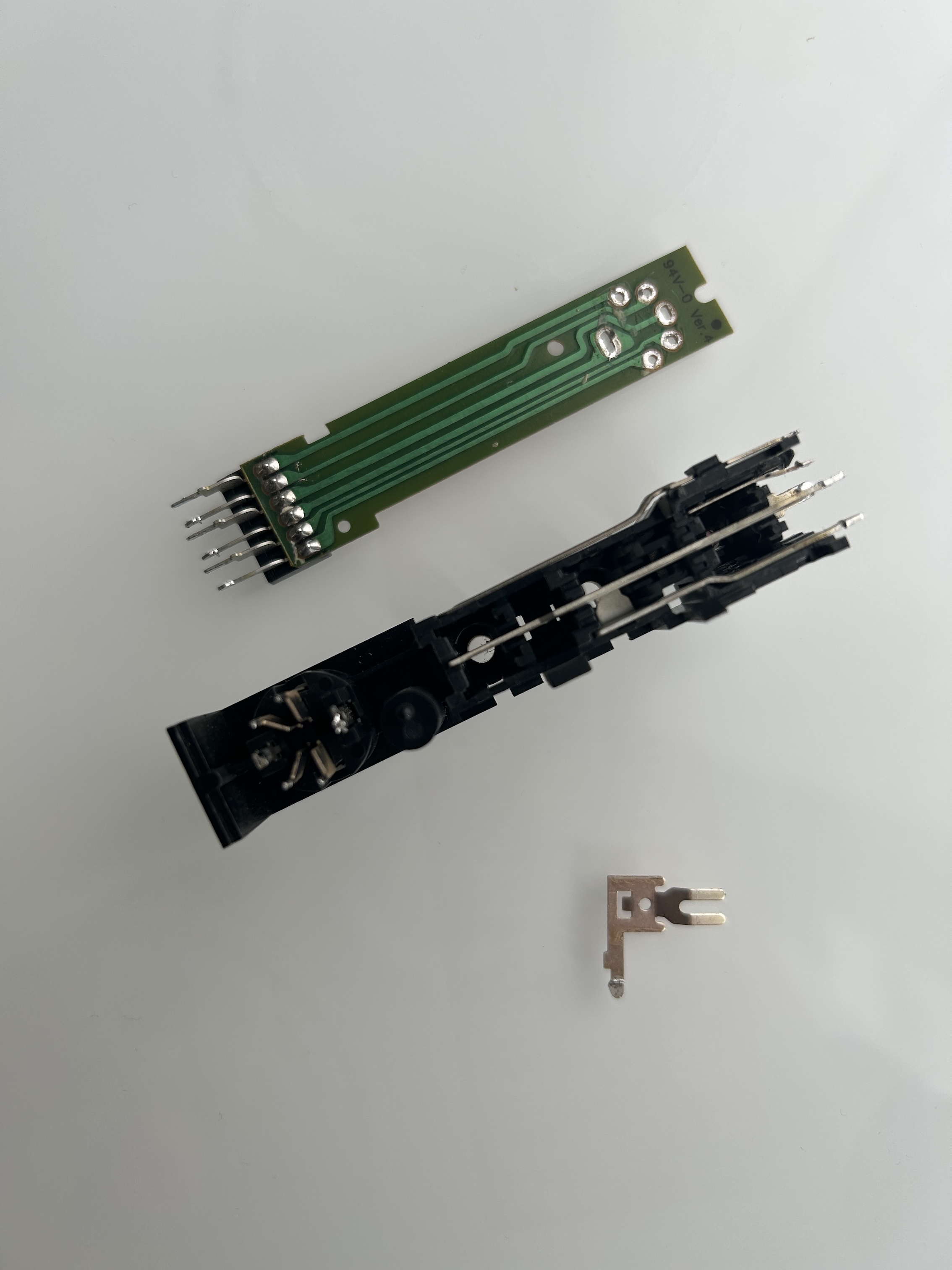
- Option 3 (High Effort, Cleanest Solution): If you have a desoldering tool, you can remove the physical clip that forces mono when nothing is plugged into the red RCA port. This is the most involved method but results in a clean and permanent solution.
Below, you'll find pictures demonstrating Option 3.

STEP 5: Connect sync and s-video detect
Finally, we have a purpose for the orange wire! In other mods, you may have seen it labeled as auxiliary or simply grounded as unused.
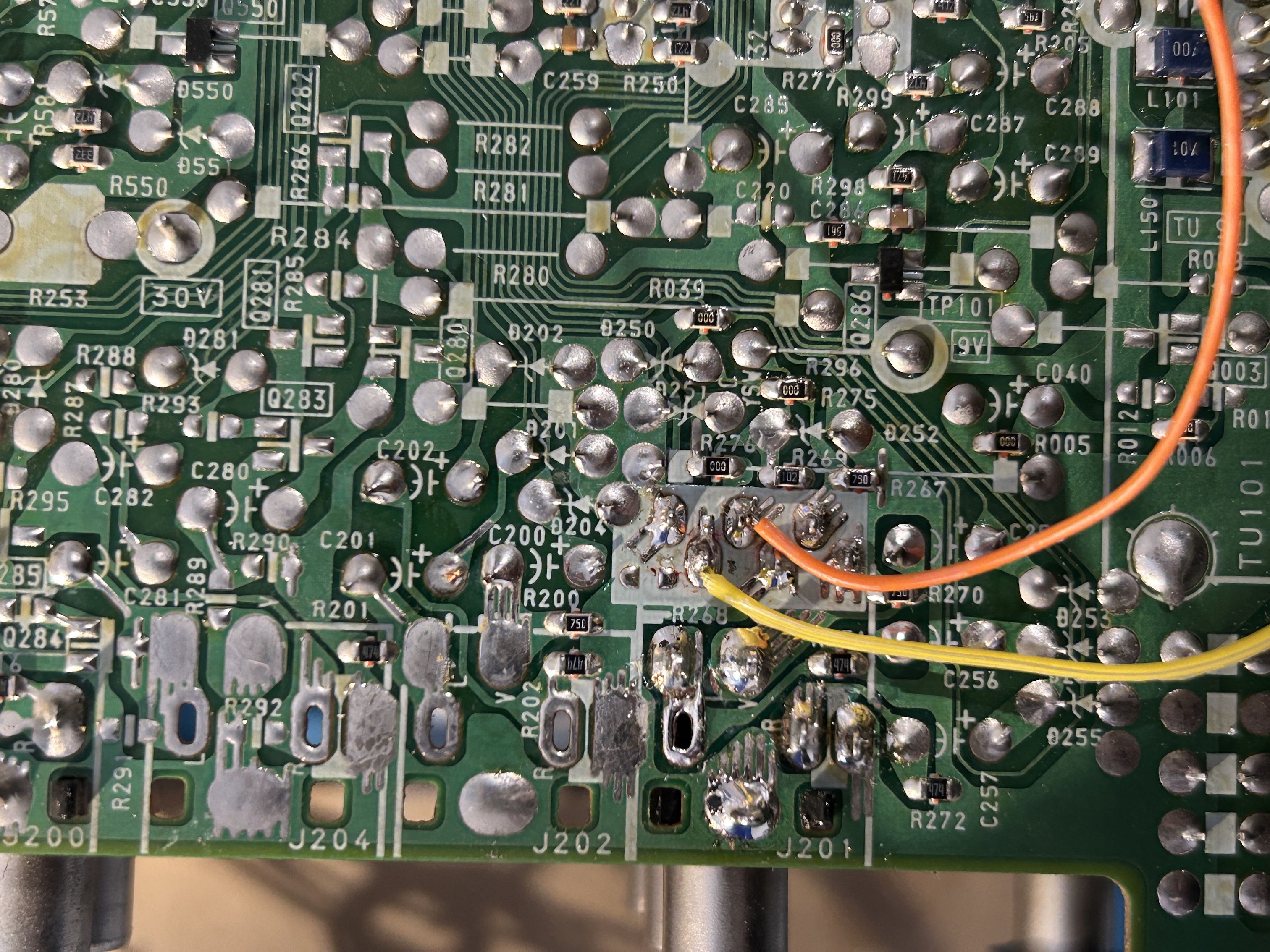
- Yellow wire: Used for sync.
- Orange wire: Functions as S-Video detect, automatically grounding when a blanking signal is detected from the SCART input.
STEP 6: Audio and ground wires
Now wire the audio wires.
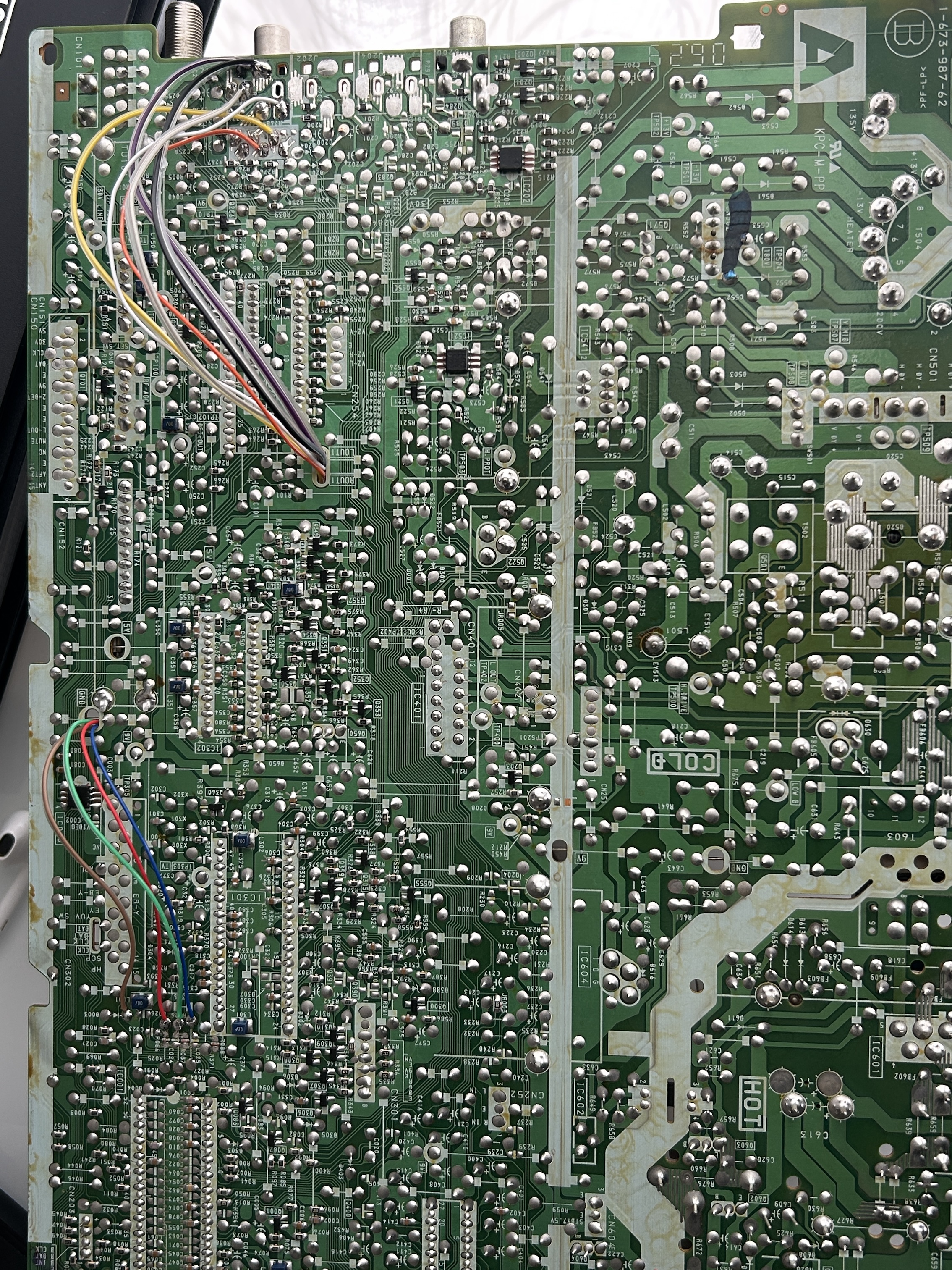
Final full mod picture.
STEP 7: Introducing the MUX 1.4B board.
Latest v1.4B board packs some useful features:
- Automatic S-Video Detection – Uses a PN2222A transistor to handle S-Video detection, eliminating the need for a dummy S-Video plug, which was a hassle.
- Auxiliary RGB Port – Adds an additional RGB input, allowing for an extra SCART or 8-pin mini DIN connection.
The board is the same size as the 1.3B/1.3C models.
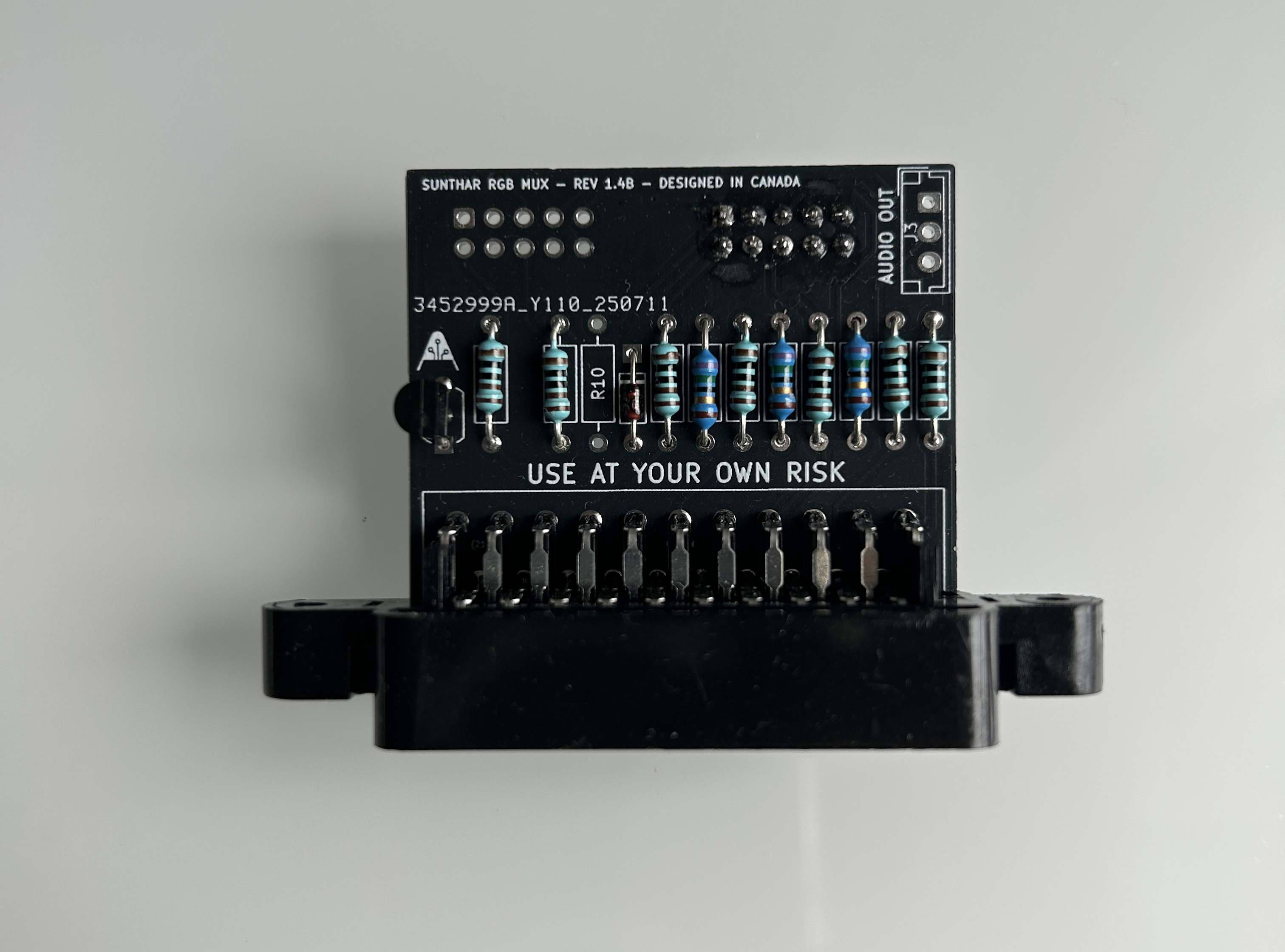

STEP 8: Build your MUX board
Below mod uses the RGB mux board. This is optional, but will make your mod easier and stable. You can also create the circuit presented in the schematics above without the board. Please also checkout the precalculated resistor values.
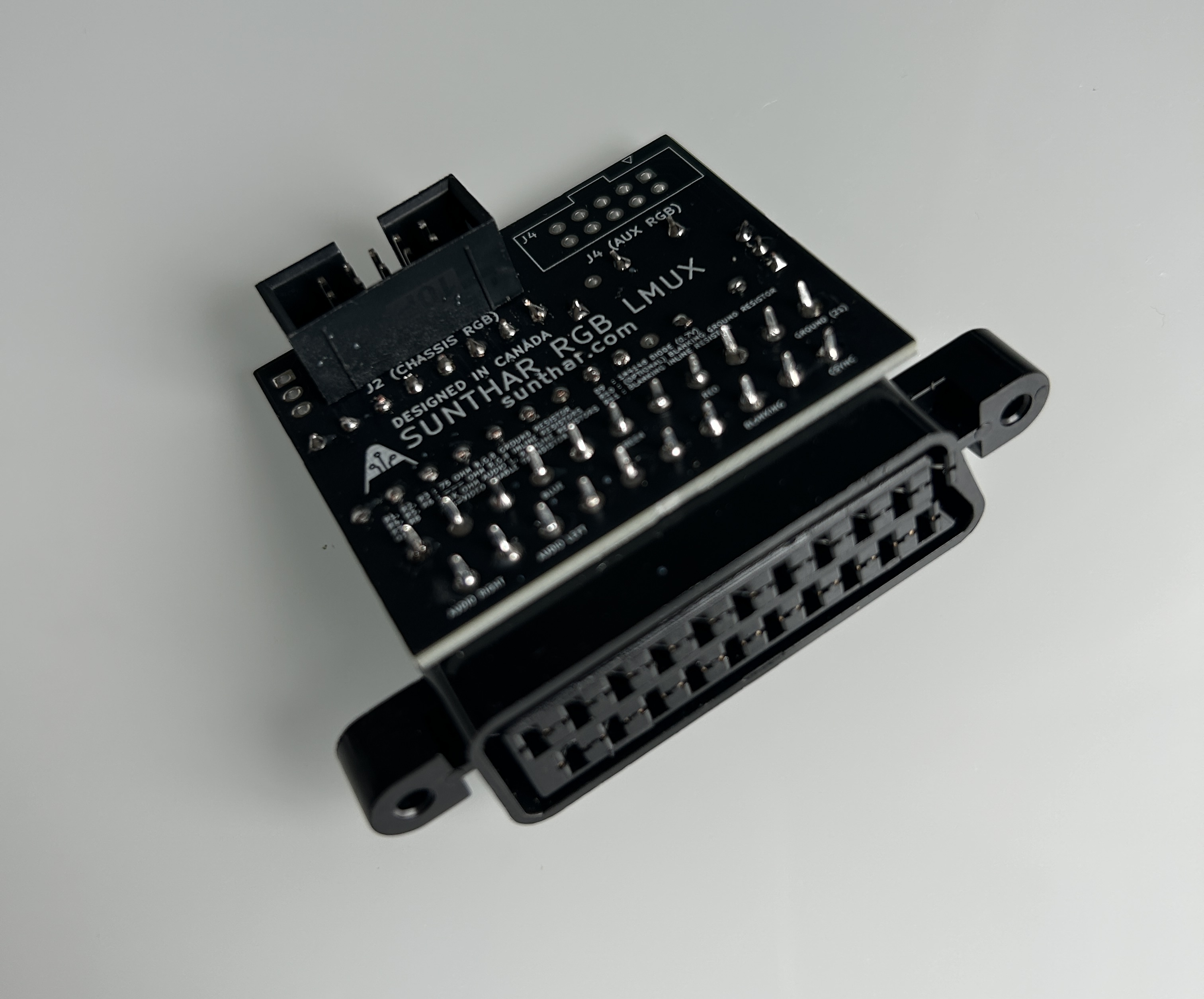


You can connect a second XRGB input using the auxiliary input through a 10-pin IDC connector on this board.
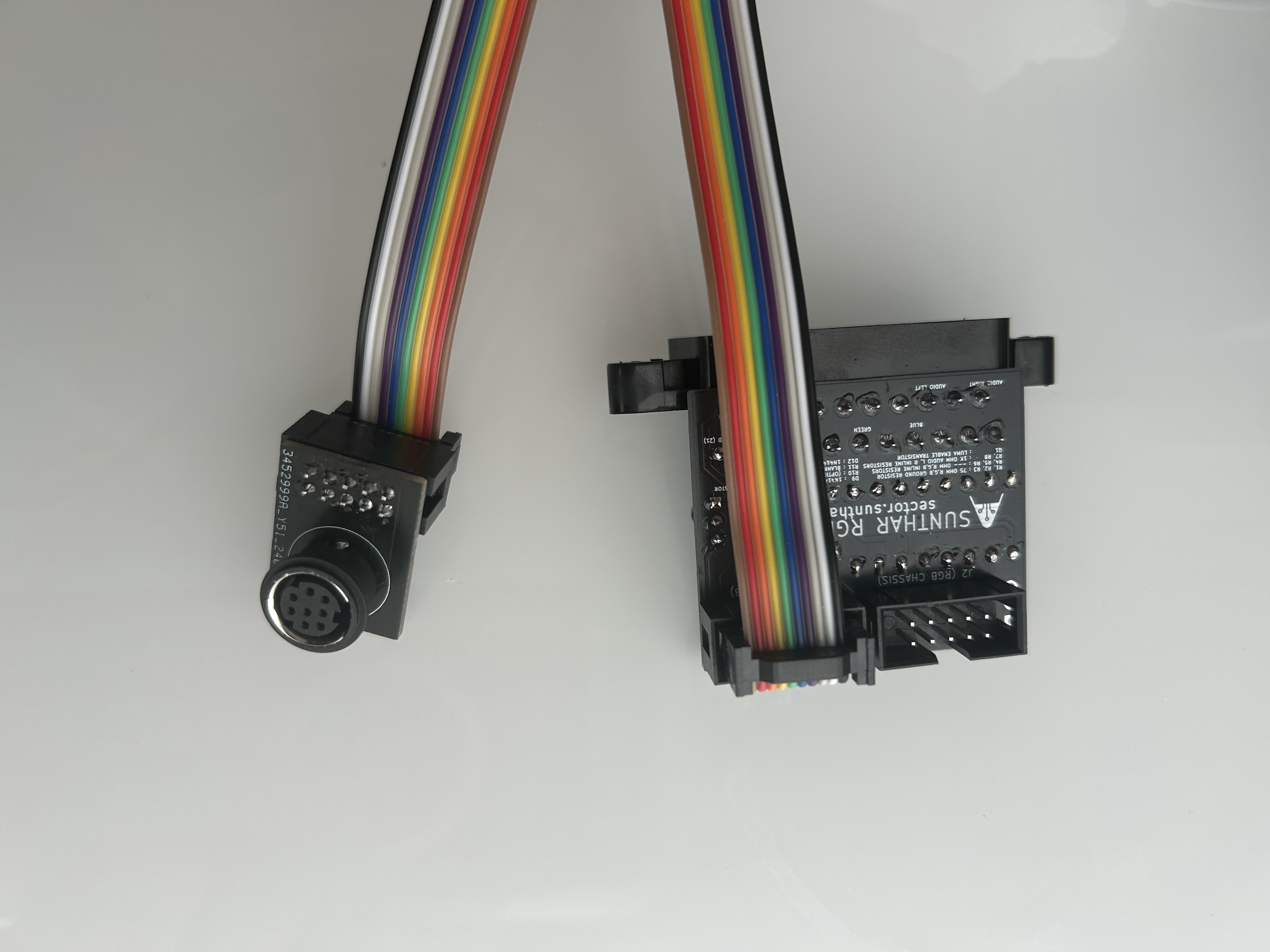

Additional Pictures
I had my boards loose during testing. Be extremely careful to avoid applying pressure on the chassis or accidentally touching the power board.